By Tracy Woolrich
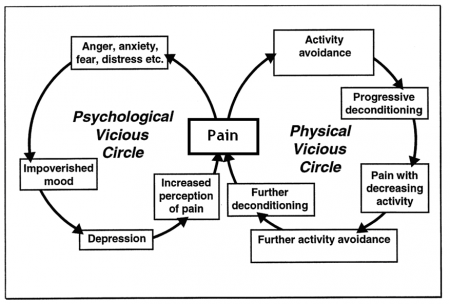
According to the American Pain Foundation, there are more than 50 million Americans living with chronic pain. What is unfortunate however is that chronic pain is often improperly treated – or not treated at all. Those with chronic pain will tell you that they feel that there is a war being waged against those who are truly in pain. The answer is to find treatments that work, empower yourself and educate those in the community.
As a nurse with more than 30 years of experience I have witnessed more than my share of pain. During my student nurse days I remember the days of “Brompton’s Cocktail”. It originated in London’s Brompton Hospital and was a concoction made with morphine, cocaine, alcohol and chloroform water. It gained popularity in the 1970s through the Hospice movement with support of Elisabeth Kübler-Ross. However, with advancements during the 21st Century it no longer exists. I personally am glad, as from what I witnessed it did appear to reduce the patient’s pain however at a cost of the ability to have a level of awareness. The patient would be nearly in a coma from sedation. We have come a long way in the ability to control pain effectively. Obtaining and maintaining a proper dose however is another story.
In 2006, the American Pain Foundation surveyed their members and discovered that over 60 percent experienced breakthrough pain while taking routine pain medications. In addition, 75 percent also suffered from insomnia and depression. Activities of daily living were affected with over 25 percent indicating that even driving a car was too difficult to do.
 That organization developed the Pain Care Bill of rights and encouraged patients to take an active position in their treatment plan. In my previous position working with chronic pain patients, I would frequently obtain guides and resource items from them to share with their healthcare providers.
That organization developed the Pain Care Bill of rights and encouraged patients to take an active position in their treatment plan. In my previous position working with chronic pain patients, I would frequently obtain guides and resource items from them to share with their healthcare providers.
In 2011, the Affordable Care Act required the Institute of Medicine to do a study about pain management. In that study it was reported that more than 100 million Americans are suffering from chronic pain. That is staggering and the highest numbers to date.
Despite the growing number of people that are in pain, the war on drugs rages on and in its path there is a tremendous amount of collateral damage. Patients that are truly in pain suffer, and organizations that become advocates and partners cannot sustain themselves. Regrettably in May 2012, the American Pain Foundation dissolved their organization due to lack of funding. They transferred a good deal of their education to other organizations and support groups in hopes of continuing their cause.
Their Pain Care Bill of Rights was a groundbreaking proposition in my opinion. It was an attempt to empower those in pain to take an active role in their care. One of the key concepts was the right to have your pain reassessed regularly and your treatment adjusted if your pain has not been eased.
Because of society’s drug addicted behavior, there have been more and more restrictions placed that are making it difficult for those in chronic pain to obtain relief. Misguided state and federal policies are restricting access to appropriate medical care for people in chronic pain. It is deterring even the most compassionate medical providers from treating anyone with pain conditions for fear of governmental scrutiny and penalties.
Better ways to manage pain are continually being developed. With relief as the goal, patients usually try various pain management techniques (often in conjunction) before they determine what works best for them. It is a very individual thing and may change over time.
Medications
There is a myriad of available medications that can be prescribed. From over the counter analgesics like NSAIDS (Motrin and Aleve) to Narcotics (Morphine, Hydrocodone, Codeine). While pain medications will assist in reducing the pain they do little to change the cause other than perhaps NSAIDS that may reduce swelling. As time goes on doses are often increased due to tolerance and often there are side effects such as constipation and stomach upset.
Exercise
Exercise can assist with pain relief in individuals with arthritis. Yoga, tai chi and water aerobics are all very helpful. Some with Fibro and chronic headaches may find the stretching portion helpful.
Massage
Massage can reduce pain, increase tissue circulation, relax tight muscles and reduce swelling. In addition it can reduce anxiety and depression and help promote a better night’s sleep. Patients with headaches, arthritis and traumatic injuries will find this helpful. Those with Fibro may find it too painful. Cranial-Sacral work or Reiki may be more appropriate.
Biofeedback
This uses a combination of combination of visualization, relaxation, visualization, and feedback from a machine that may help you to gain control of pain. Electrodes are attached to you and plugged into a machine that measures your muscle tension, blood pressure and heart rate. In time you are able to control your thoughts and tension and thus reduce pain and anxiety. It is very effective with headaches.
TENS Units
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation uses low voltage electrical stimulation to block pain signals to the brain. This is accomplished through the placement of small electrode patches on the skin that is attached to a portable unit that emits a small electrical charge. It is used for pain in a localized area. Individuals with nerve pain such as diabetic neuropathy or trauma may find this useful.
Meditation / Relaxation
Through the use of guided imagery and meditation techniques, muscles can have reduced tension and general relaxation. Those with all forms of pain will find this helpful especially headaches and nec/back pain.
Deep breathing
Yoga type diaphragmatic deep breathing involved clearing your mind and focusing on slow deep breaths that are rhythmic. This method of breathing involves breathing in and out, slowly, deeply, and rhythmically. It is through its process of inhaling through the nose and exhaling through the mouth you can release tension and induce relaxation. All those in pain will find this helpful.
Water Therapy
Warm water baths or hot tubs can be soothing and relaxing for muscle and joint pain. Water aerobics is often easier on the joints and can increase range of motion. Patients with arthritis and fibromyalgia may find this helpful.
Heat
Hot showers or baths, hot packs, heating pads and paraffin wax baths to hands and feet are especially helpful with arthritic pain.
Cold
Cold therapy is a preferred treatment for some people as opposed to heat therapy. Most chiropractors will advice to use cold to reduce swelling and numb the pain to local injuries. Cold compresses or the simple act of wrapping a plastic bag filled with ice cubes, or frozen gel packs can be applied locally. Those with Reynaud’s should avoid the cold.
Pain Management Clinics
Pain clinics are for those who cannot be helped by medical and surgical treatment options by their primary doctors. It usually involves prescription drug management, physical therapy, nerve blocks and relaxation therapy. Often primary care doctors will refer you to such a clinic for pain management if you suffer from chronic pain. This is twofold. It may help to reduce your pain while allowing the attending doctor to eliminate having to explain his pain prescriptions to state and federal agencies!
Support Groups
Sometimes connecting with others that have similar circumstances can not only provide a wealth of information but inspiration to keep going. Only another person experiencing the same level of struggle can understand.
Take home message
Encourage your health-care provider to inform you about the possible causes of your pain, and possible treatments including alternative therapy. Request to have your pain be reassessed regularly and your treatment adjusted if your pain has not improved. Request a pain management referral if your pain does not subside.
Are there other methods you have used to reduce pain? Please leave a comment and explain your experience.
Complete Article HERE!
















 Famous Hanging Coffin Sites :
Famous Hanging Coffin Sites :