In a Boston ICU, staff members orchestrate goodbyes over Zoom and comfort patients who would otherwise die alone.

by Sarah Zhang
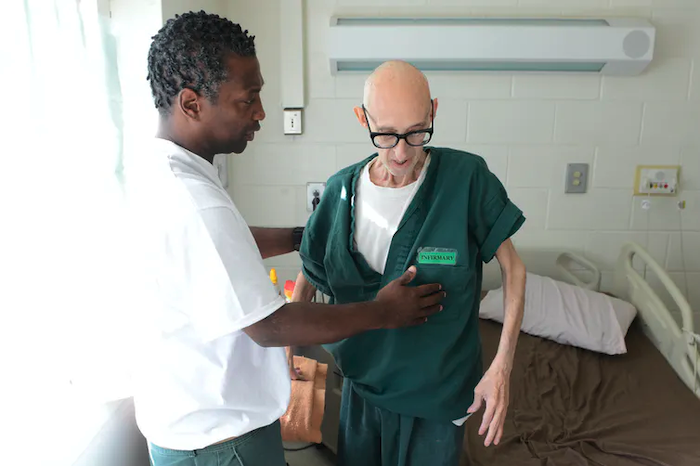
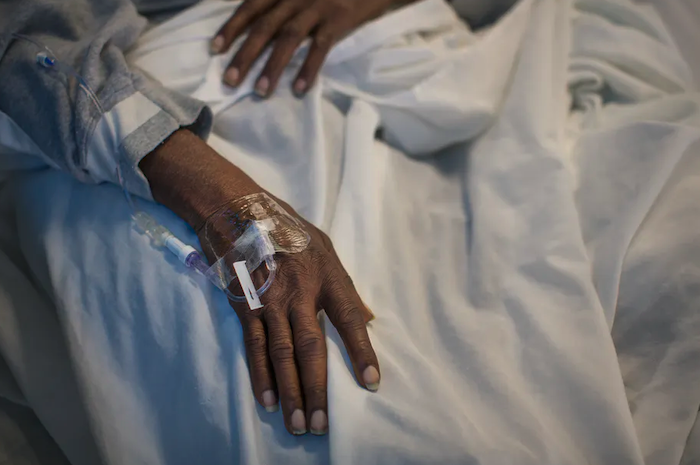
When the coronavirus came to Boston, doctors at Brigham and Women’s Hospital noticed how silent certain floors became. Any patients who could be discharged were discharged. Anyone who could stay away stayed away. “The hospital had this eerie quiet,” says Jane deLima Thomas, the director of palliative care at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Dana-Farber Cancer Institute. But in the intensive-care units set up for COVID-19, machines beeped and whirred in room after room of the sickest patients. Those patients were sedated, intubated, and isolated. Many of them would die.
Palliative care is about providing comfort—physical and emotional—to patients who are seriously ill, including those who may be close to death. Before the pandemic, deLima Thomas’s team worked with patients with kidney disease or cancer or heart failure, but this spring, they all switched to COVID-19. They embedded themselves in the ICUs. Palliative care is a field especially invested in the power of a hug, a steadying hand, and a smile. In other words, palliative care is made especially difficult by a virus that spreads through human contact.
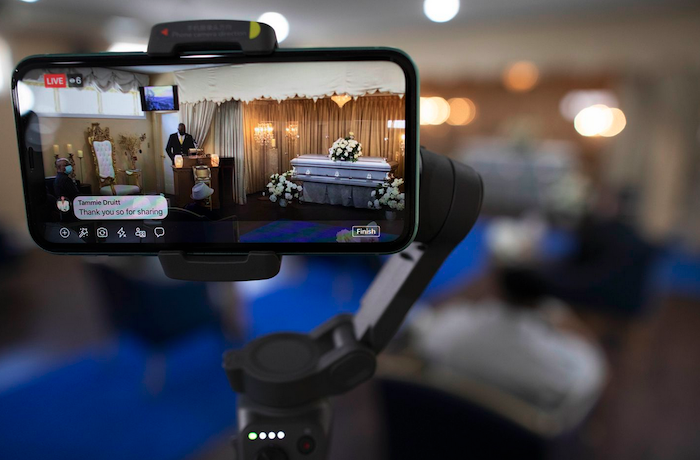
The first day the palliative-care doctors walked into the ICUs, Thomas says, “we felt like tourists.” They were dressed in business casual, while their ICU colleagues raced around in scrubs and masks. But the palliative-care team—which includes physicians, nurses, chaplains, and social workers—found ways to integrate themselves. In the early days of the pandemic, when protective gear was scarce, no visitors were allowed. Palliative caregivers, along with ICU nurses, held iPads cocooned in plastic bags so families could say goodbye on Zoom. They were sometimes the only one in the room when a patient died, otherwise alone. I interviewed several members of the Boston-based palliative-care team, and their stories, which have been condensed and edited for clarity, are below.
/media/img/posts/2020/06/rule_3/original.png)
Samantha Gelfand, Fellow
In the ICU, the most immediate thing is the personal experience of walking down the hall. Nearly every patient’s room, the door is closed, and the patient is alone. And they’re often on their bellies for prone positioning. You can’t even see their faces often.
Seeing anyone who is critically ill with a breathing tube, lots of monitors and beeping, it’s not easy. When we facilitate Zoom calls with family, I say, “Listen, it may be alarming to see that your loved one has tubes and tape and monitors on their head.” They may have soft wrist guards on their arms to stop them from trying to take out their own tubes.
It doesn’t always work. I did a Zoom call with seven family members. The patient was a man in his 50s and he had seven kids, and they ranged from 18 to late 20s. I told the siblings what I could to prepare them, and still I’m holding the iPad and they start wailing. There’s a visceral experience of just devastation.
As someone’s who lost my own parent, I think wailing is appropriate. I let them. I actually think holding the silence and bearing witness is the right thing to do first. It’s very uncomfortable to watch, but I think it’s misguided to try to hush or try to shorten it. How do you comfort someone on Zoom? It sucks.
Our department has a reflection conference on Tuesday mornings. In COVID-19 times, we’re still doing this, but now we’re doing it by Zoom. One clinician will read the names of patients who died last week in our care. It’s very, very eerie to hear the list of names and have worked with probably half of them and not have seen their faces.
Usually when we sit in that room and we remember the dead, we are remembering what it felt like to talk to them, what they looked like. And this, it’s like we’re remembering what it felt like to think about the patient or what their family members’ voices sound like. I really missed the times when I could think of a face the patient made or a comment that they said. It feels like a new way of grieving.
/media/img/posts/2020/06/rule_3/original.png)
Ricky Leiter, Attending Physician
COVID-19 doesn’t just affect individuals. It’s affecting families. I’ve had a couple cases where a married couple is in the ICU, next to each other. I was talking to a daughter whose parents were both intubated in the ICU. They were in their 70s to late 80s. Her father wasn’t doing well, and we were asking, “Should we try to resuscitate?”
I remember her saying, “I can’t think about the hard stuff right now. This is all too much right now. I can’t do that.” And of course she couldn’t. How could she? Her parents were relatively healthy before they came in. It was the suddenness of all this. In my normal palliative-care practice, those are patients who have been sick for a while. They have been diagnosed with a serious and life-limiting illness. A lot of COVID-19 patients are otherwise pretty healthy; maybe they have high blood pressure. This is an entirely new universe.
One of our fellows did five or six tough conversations like this with families in one day. I had a day like that early on. Our team walked back to our office, and everyone there asked what happened to us. We were so shell-shocked, and it felt like we were having the same conversations over and over. I don’t normally have six conversations where it’s the same disease, the same coronavirus.
/media/img/posts/2020/06/rule_3/original.png)
Reverend John Kearns, Chaplain
My brother died 30 years ago this September. It was a life-changing experience and really oriented me into the life of loss and grief. He died of AIDS, which seems so similar now with the fears surrounding an illness that wasn’t well understood. People then were afraid to touch him or hug him. My parents were very dedicated to his care. He died at home in our bedroom that we shared as brothers.
It’s natural for people to take care of their loved one when someone’s sick. Being present for someone is part of what helps people get through it. They’re participating in some way. During this, the families have none of that participating. The first few weeks of COVID-19, we didn’t go inside the patients’ rooms. Now that we have more protective gear, they’ll let us go in, and the department has developed an iPad ministry to connect patients with family who can’t be at the bedside. Sometimes the family will email photographs and we’ll print them out and hang them in the room—photographs of the patients’ kids, wife, spouse, partner. Whether these sedated patients can see or hear is questionable, but the family gets to see, or the family gets to speak to them.
I’ve spent as much as two hours in a patient’s room. I’ve gently wiped the forehead of a patient. I’ve led prayers with the family over the patient. And they will ask us to hold their loved one’s hand. Often there’s a hope to see there’s a response, whether it’s a simple squeeze of a hand, a blink, the movement of the head—anything that gives them hope that their loved one is going to make it.
When the family wants to be seen by the patient, then you have to do the reverse camera and then hold it in such a way that they can see the patient’s face. You’re trying to orchestrate this intimate moment and sacred moment, and you’re fumbling with this iPad. Where is the camera lens on these things? And at first, we were putting these iPads in plastic bags, like a Ziploc bag, to keep it from getting germs on it. So now it’s sliding around in this bag that’s a little too big. You also have the problem of fogging up your glasses and fogging up the shield. At times, it is hard to see the face of the person or to read something or to manipulate the iPad.
There was a Muslim patient who was dying. We have a couple imams. One is actually out of the country; he has not been able to get home since COVID-19 started. The other imam wasn’t available. When the patient took a bad turn, I got called in by Ricky Leiter. As an interfaith chaplain, we also visit everyone. I had an iPad with 20 or so family members who were all over the globe. They were reciting prayers. At one point it reminded me of church bells. All those voices all over the world, coming together at the same time.
/media/img/posts/2020/06/rule_3/original.png)
Stephanie Brook Kiser, Fellow
I’ve had family members say to me, Just please go in person and tell them in person that I love them and promise me that they won’t die alone, that you’ll be there at the bedside.
A patient I took care had been sick with COVID-19 and in the hospital for two or three weeks. He was 80 years old. His wife was just a few years younger. They had been together since they were teenagers. You can just tell in her voice that it was so hard for her to be apart from him. She said, “I can’t remember a time I’ve been apart from him for this long. I think this might be the first time since I’ve known him.” At the same time, she was living in fear in her home because she knew she had been exposed to him. Because of her age and other medical problems, she was at high risk to be at the same place he was: really sick in the ICU, with a breathing tube, not getting better at two weeks or three weeks.
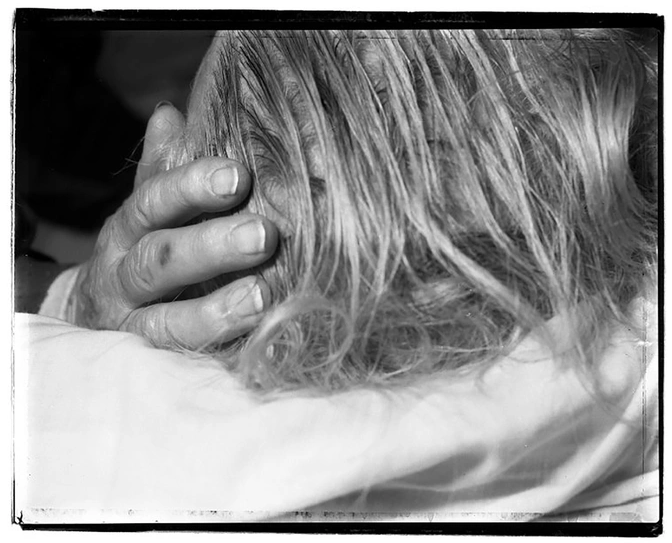
It was pretty clear medically, no matter what we were doing, he was continuing to get worse and worse and worse. We had a really difficult conversation over the phone about what his wishes would be, and it was clear to her and to their children that the biggest thing we could do was transition to focus on his comfort. We knew what that would mean is he would die pretty quickly.< With the hospitals’ changing policy, if someone is actively dying, we can now allow for a family member too at the bedside. My experience in the ICU when that’s offered, more times than not family members actually say no, that they don’t actually want to come to the ICU. There’s a real infectious risk to them, and I’ve had a lot of family members say, “I don’t know that I want to see them again the way they are now. I want to remember them the way they were before.” The wife was in such distress and despair over the idea that she was so physically close in Boston but it wasn’t the right decision for her to come into the hospital. I spent a lot of time and I was even grasping at things: Can I arrange a Zoom call? Maybe I can record a video and send it to you guys? And the family was saying, We want to remember him in a different way.
They said, We just want you to go to his bedside and hold his hand so that he knows he’s not alone. And I did that over the course of about 15 minutes. He died pretty quickly.
I’ve been part of a lot of deaths of patients in palliative care. We don’t see a lot of death like this—without any family members present. We aren’t used to being that person at the bedside, trying our best to provide the comfort that a family member’s presence would provide and feeling inadequate in that at best. Afterwards I gathered his nurses and respiratory therapist and we talked. Everyone agreed it was unlike anything they had been part of.
It was the first time I had touched him. And in the ICU, probably one of the only times I’ve physically touched the patient.
/media/img/posts/2020/06/rule_3/original.png)
Natasha Lever, Palliative-Care Nurse
I’ve been a nurse practitioner for seven years, and I was hired at Brigham to do heart-failure and palliative care. Literally the week after I started, COVID-19 happened. They had this whole very carefully planned out 12-week orientation, and I got a phone call from our director, Jane, and she said, “Either we’re going to keep you at home for the next few months or we’re just going to put you in the ICU.” I kind of got thrown into the deep end.
I went into nursing because I love to be at the bedside and with patients. Not having families and loved ones at the bedside was probably the most difficult part of all of this. It felt so wrong to us that families were having to make decisions about withdrawing care when they haven’t seen their loved ones.
I remember the one that hit me the most was a woman whose son had given her COVID-19. He had been quite ill himself, and he had recovered. The immense guilt that he felt was so profound. He kept saying—he’d obviously been watching the news—“Please, don’t throw her in a body bag if she dies.” He kept talking about how they had been so excited they were going to move into a house together and he was going to buy his first house. He had plans for her and just wanted her home so badly. She passed away and it was very difficult.
That was one of my first cases. And this was week two of my job as a palliative-care practitioner.
I remember the first day I was in the ICU, it was completely chaos. It was very loud, lots of people. Almost this adrenaline rush you felt. A couple of weeks in, things sort of settled down. Now the ICU numbers are down. I had a really strange feeling when they were closing down the COVID-19 ICUs. I walked down the hallway and it was dark and all the rooms were empty and clean and there was no one there. Two weeks ago, this was one of the most busy, chaotic places in the hospital and there was just this silence. No alarms, and no people. It was almost as though, Is this a dream, did that really happen?
Now I have just started doing the orientation that I was supposed to be doing. I’m going back to the hospital. I’m extremely excited to be at the bedside. I have never been so excited to talk to a patient in real life.
Complete Article ↪HERE↩!