A Tim Boon Poem

Tim Boon, RN is the CEO of Good Shepherd Community Care in Newton, MA. Share this poem with ALL the loved ones.

The Amateur's Guide To Death & Dying
Enhancing Life Near Death

Tim Boon, RN is the CEO of Good Shepherd Community Care in Newton, MA. Share this poem with ALL the loved ones.

By Matt Pickles
Maths, science, history and death?
This could be a school timetable in a state in Australia, if a proposal by the Australian Medical Association Queensland is accepted.
They want young people to be made more familiar with talking about the end of life.
Doctors say that improvements in medicine and an ageing population mean that there are rising numbers of families facing difficult questions about their elderly relatives and how they will face their last days.
But too often young people in the West are not prepared for talking about such difficult decisions. There is a taboo around the subject and most deaths happen out of sight in hospitals.
Pupils might have reservations about lessons in death education.
But the Australian doctors argue that if the law and ethics around palliative care and euthanasia were taught in classrooms, it would make such issues less “traumatic” and help people to make better informed decisions.
Queensland GP Dr Richard Kidd says young people can find themselves having to make decisions about how relatives are treated in their dying days.
“I have seen people as young as 21 being thrust into the role of power of attorney,” he says.
Their lack of knowledge makes it a steep learning curve in “how to do things in a way that is in the best interests of their loved ones and complies with the law”, he says.
He says the taboo around death means that families usually avoid discussing until it is too late. Most people do not know how their relatives want to be treated if the worst happens.
“So we need to start preparing young people and getting them to have tough conversations with their loved ones,” he says.
“Death lessons” could include the legal aspects of what mental and physical capacity means, how to draw up a will and an advanced care plan, and the biological processes of dying and death.
These topics could be incorporated into existing subjects, such as biology, medicine, ethics and law.
Dr Kidd says education around death would help countries like Australia, the US and the UK follow the example of Mexico, where death is an important part of the culture and even celebrated in the Day of the Dead festival.

He gives the example of Ireland, where he says wakes held after a death can be “joyous occasions”.
Introducing a culture of openly discussing death could even change where we die, according to Dr Kidd.
The vast majority of Australians die in hospital, even though many people say they would rather die at home with their family around them.
“Only 15% of people die at home but in the case of many more people, they could have died at home rather than hospital if there had only been a bit of preparation,” says Dr Kidd.
A hundred years ago it was very normal for people to die at home. but modern medical technology allows life to be prolonged in hospital, even though the patient might not have great quality of life.
“People may decide that at a certain point they want to be able to die at home in comfort rather than being kept in hospital,” he says.

The proposal for lessons in death has now been put to the Queensland education authorities and Dr Kidd hopes the message reaches other parts of the world.
“Our main aim is to get young people to start having those conversations with their parents and grandparents to learn more about how they want to die so that they know the answer when they need that information in the future,” he says.
“It should be seen as a positive and proactive thing – information and knowledge can be really empowering to people.”
So perhaps this is something to bring up over your next family Sunday lunch.
It might not be an easy conversation but it could be a matter of life and death.
Complete Article ↪HERE↩!

The old man lies in the hospital bed, drawing his last, rattling breath as he fades away from life.
The film camera, positioned just next to him, keeps rolling. We see the nurses move him to another room before they gently clean his body.
“Nobody wants to die but it’s a natural thing, we are biologically determined to die,” says documentary maker Steven Eastwood.
His film, Island, lays bare the dying process by filming four people with terminal illnesses.
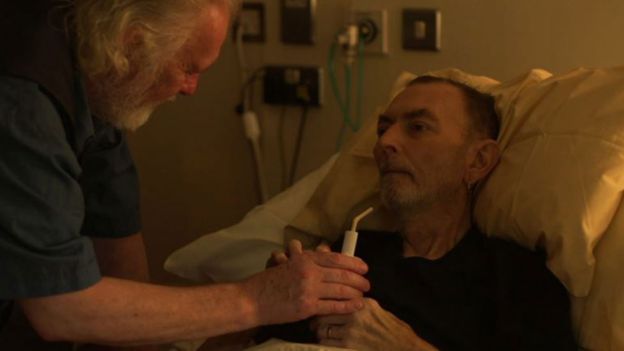
“Death is seen as a shameful thing – we think we’re a progressive society, but we repress and deny death,” Steven says.
“We’re no better than the Victorians.”
He was a quiet onlooker during the last year of his subjects’ lives, filming them in their homes before they became part of the daily rhythms of life in a hospice.
“To say you don’t want it to happen, you’re putting off facing something,” he says.

“We need better death awareness to be more familiar with our mortality. I don’t think that’s ghoulish.”
The documentary came about after Fabrica, a gallery in Brighton, commissioned a film about end of life.
The London-based film-maker’s proposal was accepted, and he managed to get access to film in a hospice on the Isle of Wight.

He speaks fondly of his time there, saying: “These are four people I really cared about – Alan, Roy, Mary and Jamie; three were in their 80s and one was in his 40s.”
Steven regularly made the five-hour journey to the hospice, including the boat trip to the island, which features in the slow, often hypnotic imagery of the documentary and its trailer.
He made the film after having “two quite significant bereavements – my mother-in-law and my best friend, who was the same age as me.
“So I realised I didn’t know very much about what palliative care is.”
Steven thinks we need to face the reality of death, make it part of our daily existence, so it’s less frightening.

“I think we all have an existential fear – ‘if I see someone I love who’s died, it’ll be too traumatic, it’ll replace all the images I have of them, I’ll never be able to unsee it, somehow it’ll hurt me’.
“But for me it isn’t the case, being with someone after dying, with that intimacy. I found it quite empowering and peaceful.”
He has huge admiration for the people who work in hospices, and hopes his film can “celebrate and show what palliative care is”.
“The most radical, extraordinary people in our society are the least visible,” he says.
“They’re the carers. And the care we receive at the end of our lives is extraordinary.

“These hospices which people have anxiety about going into – they’re not morbid, sterile spaces, they’re places of life.”
He says that after one of the screenings of Island, a stranger approached him, saying it had made him “less afraid of dying”.
Steven adds: “It’s not an ambition of mine, but if you can sit through the film and at the end feel uplifted, if you can make some kind of peace with something that will happen to all of us, then that’s a good thing.”
He speaks fondly about all his subjects, talking at length about Alan, whose death we see at the start of the film. Alan died of cancer.
“Alan had chain-smoked since he was 16 and he smoked in the hospice with a nurse lighting his cigarette. But he wasn’t dying of a smoking-related cancer.
“This is part of what palliative care is – helping someone smoke until they die.
“The doctors felt that if he hadn’t been smoking he would have died several weeks earlier – he was living to smoke.”
Alan invited him to film his last moments.

“The second time I met Alan, we had a connection, he said, ‘I think you’d like to stay with me all the way through and I think that would be great’.
“He wanted to do something radical with his death, he felt quite radical about his life.
“He believed our tissue is just a vehicle and we translate into something else.
“As far as he was concerned, there was no self-consciousness around his image, he thought participating was a way of marking something of his philosophy. He became my movie star, he was like my Burt Lancaster.”
Steven recalls watching Alan die.
“His death was a long, running out of breaths. It was very peaceful and very beautiful and I felt really moved by it. I didn’t feel sad. He was really ready to die.”
Alan told Steven he had seen a man die when he was just 19, during active service in the forces in North Africa. His commanding officer was shot, and died in his arms.
“He held this man and said, ‘I saw bliss in his eyes as he died, and I knew that what we are experiencing now is not it, there’s more’.
“So for him, his death was the thing he’d been waiting for. We can’t all ask for that.”
Steven acknowledges that of course deaths can be sudden or premature, such as Jamie’s.

“Jamie had stage 4 stomach cancer and had a young family, his attachment to his daughter was so incredible.
“He wanted to die in the best way he could with his daughter, so he involved her in everything, talked about his treatment, about what it was going to be like when he’s not there.
“He’s the person who I get upset thinking about.”
The film has been used to help medics in handling end of life care, and Steven and his producer are partnered with Sussex NHS trust.
“We’ve run two sessions with trainee doctors, to use the film as a means to talk about how we speak around death and dying, and how we talk to patients.”
He’s also keen to attract a young audience as he says people in their 20s are the “biggest death deniers”.
Steven talks about the pressure to be “productive, youthful, to look good”.

“This idea that we’re terminal and have an end is too much. I’ve spoken to young people who think about their late life and say, ‘oh I just want to take a pill to end it, when I’m no longer viable I switch myself off’.
“I do think it’s challenging to confront your own mortality.”
Steven, who also volunteers at his local hospice, thinks other cultures handle death better than we do, saying in Ireland “you see a more sustained grieving process and more familiarity being around the body”.
He also talks about Latin America and Asia, where they have “a completely different attitude towards the dying process”.

“I think we need better education – we are finite, our bodies do decay, and I’ve made my peace with that.
“I hope the film can return us to some extent to our biological bodies, and say yes, everybody will die, most people will die in this way, in their 70s or 80s from either heart disease or cancer, and the care will be extraordinary.
“I don’t find that a burdensome thought. I felt poorly informed, and now I feel better informed by making the film – I hope that it will do that for people.
“We die and we don’t have to turn it into some kind of sanctum, it’s life. And I think Alan showed me that, so yeah, I was very, very fortunate to be invited to film him.”
Complete Article ↪HERE↩!
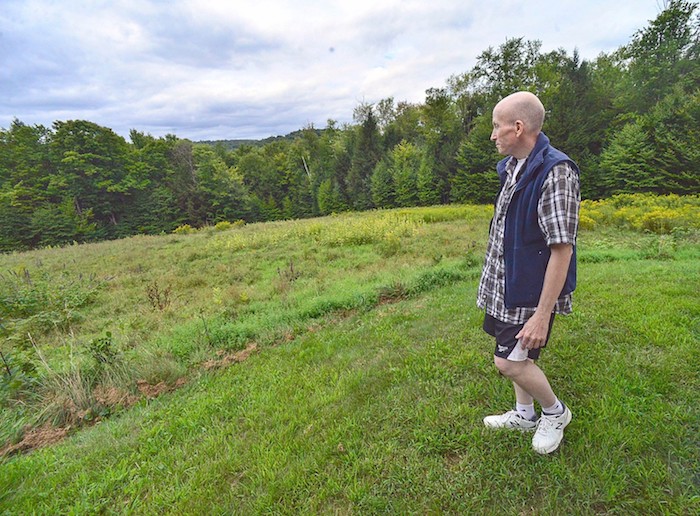

By Bob Audette
David Price is dying, but it’s not the colorectal cancer he was diagnosed with two years ago that is killing him. Doctors removed the tumor shortly after his diagnosis, but Price believes it’s only a matter of time before fate catches up with him.
Rather than let chance decree his date of death, Price, who is a psychologist with an MBA, decided to take the matter into his own hands. About a month ago, he stopped eating and next week, he stops drinking. He expects he will die a week or two thereafter. He faces his death with very little fear and a mental calmness that is peaceful and accepting.
“God has blessed me,” he said. “I have always had a deep faith. I know what’s on the other side.”
Price said he loves the life he has lived, but the current quality of his life was compromised following his cancer surgery. The surgery resulted in having what he calls “a dysfunctional rectum” and as a result, has to use a colostomy bag.
“I will never again have a normal bowel movement,” he said. “I will always wear Depends and I will always need to be close to a bathroom. If I can’t go to the bathroom properly, that’s just not a life.”
While Price said he is “supposedly cancer-free,” he has been told by his doctors he is at a high risk for a recurrence. “Plus, I have multiple health issues that could eventually kill me, including blood clots and hernias. I have epilepsy and I was falling as often as twice a day due to my medications. If I fall and crack my skull and go into a coma, where am I going to be lying for six years? Not at home. I don’t want to be in a nursing home.”
He understands that some people may judge his choice to end his life now, and many people have tried to change his mind. Price also acknowledged that while he believes he is making a rational decision based on his spiritual values and ethics, his choice is unique to him and no one else.
Act 39
In 2013, the Vermont Legislature passed Act 39, the End-of-Life Choice Law, which allowed Vermont physicians to prescribe medication to a Vermont resident with a terminal condition with the intent that the medication be self-administered for the purpose of hastening the patient’s death. Act 39 set forth conditions for the patient and doctors to be in compliance with the law, including that the patient be capable of making his or her own informed decision. But because he doesn’t have a terminal illness, Act 39 doesn’t pertain to Price.
“I don’t fit the criteria as much as my doctors might like, and they tried their best to convince me otherwise, but all of my medical providers have been supportive of my decision,” said Price, who doesn’t consider what he is doing as suicide. “It’s not extending my death.”
Betsy Walkerman, president of Patient Choices Vermont, which successfully advocated for the passage of Act. 39, said it would be a mistake to conflate Price’s decision with suicide.
“An end-of-life decision is really different from a situation where someone is distressed or has serious depression,” she said. “There are people in the last stages of life who don’t qualify for Act 39 who have stopped eating and drinking. It’s a person’s own choice how to live their life and how to spend their last days and weeks. This is a decision that any person can make and doesn’t require Act 39 and permission from anyone.”
Walkerman said Price’s decision is a demonstration of how people take control of how they die.
“There are so many ways to prolong life as the medical community defines it,” she said. “But whether a person wants that kind of life … it doesn’t sit there in a vacuum. It’s part of the continuum of the evolution of medical care and people’s interest in personal choice.”
Rev. Audrey Walker, of the First Congregational Church in West Brattleboro, said she counseled Price on his decision, and while she advised against it, she understood why he decided the way he did.
“He has reached what I consider to be a very rational decision based on his spiritual beliefs and I support his decision,” she said.
Rev. Shawn Bracebridge, the pastor at Dummerston Congregational Church, met with Price but only as a friend, he said, and he supports Price’s decision as well.
“His decision is his and his alone and it’s grounded in his spirituality,” said Bracebridge.
Medical ethicist weighs in
Arthur L. Caplan, head of medical ethics at the NYU School of Medicine, noted that doctors are required to have a patient assessed if they believe he or she is depressed or otherwise rendered incompetent by a mental health illness.
“If that’s not a concern,” said Caplan, “if Mr. Price is rational, he retains the right to refuse medical treatment. He doesn’t have to accept intervention. In fact, he has a fundamental right to deny an act of intervention.”
Caplan noted that people make this type of decision every day, and by example referred to a Jehovah’s Witness who might refuse a blood transfusion, even knowing it’s a simple life-saving procedure.
“Mr. Price’s doctors might have a good sense that their patient is well aware of what he is doing, that he is coherent and that he is able to comprehend his choices,” said Caplan. “It is the doctor’s duty to try to talk him out of, offer pain control or tailor your care, but that doesn’t mean the patient will be persuaded.”
Caplan also noted that some people with chronic illness who take their own lives are not as deliberate as Price appears to be, who has planned his death in advance after consulting with doctors, his therapist and members of the clergy.
Even when someone has a diagnosed mental illness that is affecting his or her decisions, said Caplan, it can be very difficult to stage an intervention.
“It’s very difficult to force feed someone,” he said. “They could pull the tube out. You would probably have to tie him down. It’s very hard to do with an unwilling person.”
A doctor might refer a patient for a psychological assessment, which could result in a court hearing to decide a person’s fate, but Caplan said courts are often reluctant to get involved in end-of-life decisions.
“Our society leans very hard on honoring individual autonomy,” he said.
Just the same, doctors who are trained to preserve life at all costs do not take it lightly to step aside and let a non-terminal patient die, said Caplan.
“It’s a challenge for them, because they are thinking they can manage epilepsy and they can manage blood clots,” he said. “But they are also trained to respect a patient’s choices.”
“The real issue,” said Caplan, “is not so much is he competent, but does he need spiritual support? Is his quality of life bad because he is depressed or doesn’t have companionship? Does he have friends and a social life?”
If anything that can still be expected from Price’s doctors, said Caplan, is that they stay in contact with their patient and keep checking with him in case he changes his mind and needs medical care.
“I couldn’t have been evaluated more in the past two years,” said Price. “If I was suicidal I wouldn’t be doing this right now.”
Price said his own decision has been informed by his years of practice — especially in the days when there was no treatment for HIV/AIDS — helping people confront their own mortality and helping them “untangle suicide from their sincere desire to end their lives. Most were facing horrible continued pain and suffering.”
‘We don’t know how to live in this world’
Price, originally of Dallas, moved to New England 16 years ago with his then-husband, Michael Lefebvre, to be closer to Lefebvre’s parents, who were ill. They lived in Gardner, Mass., until their divorce in 2008, when Price moved to what he calls his “mountain home” in Westminster West.
“I had all these wonderful plans for retirement,” he said. Instead, said Price, since his surgery he has been diving into his spirituality, studying up on Buddhism and Christianity.
“It’s helped me to realize this is all an illusion,” he said. “All of these material things we grab on to, that we think bring happiness, they don’t bring happiness; they bring us pleasure, momentary pleasure. But they also bring us pain and cost a lot of money. We don’t know how to live in this world. We copy others. I went through all that. I know the lifestyle and it did not lead to happiness.”
Though he has always been a spiritual man, he was not a regular attendee of church. His parents, who still live in Dallas, are Southern Baptists, a denomination with which Price has issues.
“There is a lot of negativity,” he said. “I don’t believe in hate. They don’t call it hate. They think they sit in judgment of the world.”
His parents also did not accept the fact that he is gay. “My family was disappointed in my whole life, not becoming a Baptist and becoming a psychiatrist. To them, mental illness is a sin that can be prayed away.”
The United Church of Christ accepts him as he is, said Price.
“They also accepted me as someone who sees ghosts,” he said. “I didn’t expect to be accepted, but they were like, ‘Yeah, Jesus saw and spoke to spirits.'”
Price firmly believes that all humans have psychic abilities, but not everyone chooses to accept that or practice those abilities and he also believes humans need to be physically close to the earth, touching it with bare flesh as often as possible.
“There is so much energy from nature that we are blocking with our concrete and steel,” he said, which is another reason he wants to die in his mountaintop home and not in a hospital or a nursing home. “I want to be here where I am absorbing the energy.”
‘A very spiritual man’
Price granted his therapist, Supriya Shanti, permission to speak with the Reformer. Shanti has been his therapist since the time Price was diagnosed with cancer.
She said his decision to end his life is not out of character, nor does she believe is it influenced by any mental health issues.
“He is a very spiritual man,” said Shanti. “His decision is a result of his connection to his spirituality, the spirit world and god and his trust and faith in that.”
Shanti noted that Price is a well-respected therapist in his own right and his decision has been informed by his years of offering counseling to his own patients.
“It’s his personal choice,” she said. “Given how he’s been fighting for two years and continues to suffer due to his medical issues, I think it’s his right to choose for himself and I support his choice.”
However, on both a professional and personal level, Shanti said she wrestled with Price’s decision.
“I definitely feel sad on a personal level,” she said. “Professionally, it creates some conflict, because I don’t know if we kept working together, maybe he would make a different decision. But the bottom line is, whoever shows up in my office, it’s my job to support and guide them. I help empower people to make their own decisions.”
Shanti also encouraged people to call and visit Price before he dies, rather than wish they had done so after he is dead.
“David wants company and wants honest conversation,” she said. “Now is the time to visit. It’s really important, especially in the last days of life on this physical plane, to be surrounded by people who love you.”
A necessary discussion
Walkerman said Act 39 and people like Price have ignited a discussion that has been a long time coming.
“He had a discussion with his family, his doctors, clergy,” she said. “A lot of people have trouble even starting these conversations. Any story helps illustrate for people how to have those discussions, rather than suffering alone, thinking they have no choice.”
“It’s important for people who are facing health and emotional crises to take a lesson from this in that you can reach out and get support for your spiritual and emotional needs,” said Susie Webster Toleno, the pastor at the Congregational Church of Westminster West. She said that while she didn’t counsel Price on his decision, they discussed the spiritual aspects of his illness and end of life. “There are people who will answer your phone call, who will listen and provide support,” she said.
Toleno said those people include local clergy members and organizations such as the Brattleboro Area Hospice, at 802-257-0775 (Brattleboro area) 802-460-1142 (Greater Falls area) or brattleborohospice.org.
“Brattleboro Area Hospice has a lot of support for people who are in tough health situations, even if they don’t qualify for hospice,” she said.
Price said if, when he first received his cancer diagnosis, he had the knowledge he has today, he might have chosen not to have surgery to remove the cancer from his body.
“It would have been quick and easy and now here I am, extending my death. But I suspected I wasn’t going to survive. Maybe my family needed time to accept that and maybe I had amends to make. I did a lot of forgiveness work, which is the most important thing.”
If there is one last notion he would like folks to consider challenging it’s the belief that all the world is knowable.
“What we think we know it probably not even one-thousandth of what it out there,” said Price, especially when it comes to spirituality. “Philosophers have been arguing about does God exist for forever. To think that you are smarter than Plato, to me that is intellectual arrogance. Even Einstein said ‘The more I study science, the more I believe in God.'”
Complete Article ↪HERE↩!
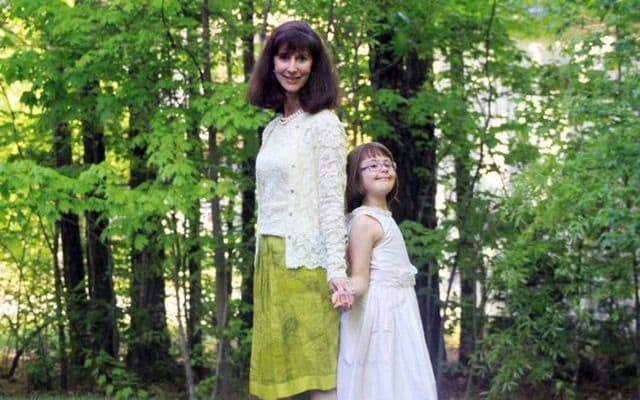

My friend Jacqueline Zinn was diagnosed with glioblastoma, a brain cancer, in 2013; she died 18 months later, at age 56, leaving behind a husband and four kids. Jacquie was a triathlete who knew a thing or two about endurance, and she managed her treatment — surgery, radiation and chemotherapy — with the same skill and organization she had brought to her work as a project manager for a drug company. Once she realized that she had only weeks to live, Jacquie began planning for the next chapter: her death and its aftermath.
And so “every night for weeks she wrote letters to our children,” her husband Doug recalled. Jacquie wrote multiple letters to each child, to be opened at different life milestones. Jacquie wanted to be “present with her kids,” he said, at each of those important moments
for what I jokingly call “The End” is not for faint hearts. War hero John McCain is said to have been disciplined and firm as he planned his funeral over the past year, including the singing of the Irish ballad “Danny Boy.” But few of us have that strength. Recently divorced, I needed to rewrite my will and my medical power of attorney as well as a host of other financial and medical documents. At almost every turn, I found myself crashing head-on into the wall of denial. Just last week, my attorney begged me to acknowledge that I was at least receiving her emails, even if I couldn’t respond to them. “Yes,” I replied, tersely. All this resistance, and I’m not suffering from any terminal condition.
That’s why Jacquie Zinn’s letters to her children seem heroic to me. After all, she did have a terminal diagnosis when she sat down to write what ended up being more than a dozen letters to her children, ranging in age from 11 to 21, and she knew her time was short. I first heard about the letters at her memorial service in 2013. This past spring, working on a book about death and dying, I reached out to her second-born son, Jerry, who was writing about the loss of his mother, to ask if he’d be willing to share his letters from her. He’d already gotten two — one soon after her death and one when he graduated from college — and after some hesitation, he said okay. Now 24, Jerry will get the final letter when he marries.
“The letters my mother left me are among the most precious gifts I possess,” he told me. “She diligently took the time, the very limited time, as her life was coming to an end to sit down and think about her children’s futures.”
So one day, in perfect cursive penmanship and blue ink after her oncologist told her she had only weeks left, Jacquie wrote her first letter to Jerry, then age 19, to be opened after she died. Here is a portion of it:
“Dear Jerry, my budding film-maker,
“I know you have a lot of emotions running through you, as I did when my father died, but I was much older than you at the time, so I really can’t begin to truly comprehend what you are feeling. I am so incredibly sorry that I had to die while you are so young and I assume it sucks for you. Perhaps you can use some of these emotions and feelings in your upcoming work(s), assuming you continue to pursue film.
“Let me assure you that I did absolutely everything I could to stay alive for as long as possible. I know you realize that having been with me at many of my treatments or tests. Plus the acupuncture, tons of praying I also did. But for some reason I just didn’t make it as one of the chosen ones to be cured. But because of what I did I’m sure I lived much longer than if I hadn’t been in good shape to begin with.
“I am incredibly proud of you for everything you have done in your relatively short life. I will be watching over you every day to see what new and exciting things you will accomplish — regardless of what occupations(s) you pursue over your lifetime.
“Do your best to support Dad and your siblings, especially during this first year as it will be the hardest for everyone. I remember that from when my father died. Time will certainly help, but it takes a long time to focus on the happy memories while the sad thoughts are more immediate and closer at hand.
“I had many fantastic years on earth, more than a lot of people, hence, I have no complaints. I survived a melanoma, car accident in the mountains of West Virginia with Uncle Jerry, car accident in Durham. So I have already lived many lives and I was extremely grateful for each and every moment. Try and live your life that way and you will be a happy and fulfilled human being.
“I love more than you will ever know, my dearest Jerry.
“Love, Mom.”
On the day Jerry graduated from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill in 2016, Doug handed over letter No. 2, written with the same pen, on the same type of note paper.
“My sweet dear Jerry,
“Well — this is it — a big milestone in your life — college graduation! Congratulations. I am so incredibly proud of you no matter what your major or minors. I know you made it worthwhile and got just exactly what you wanted to out of the experience. I know you learned an incredible amount about subjects and probably an even greater amount about people.”
Jerry said that at various times during college he had considered dropping out, but “knowing that I would never receive that letter if I did not graduate was a very strong influence in keeping me in school. The letter was a motivation for which I will be forever grateful.” Knowing Jacquie as I did, I’m certain that was part of her master plan.
In the second letter, Jacquie signs off with these words: “I am watching over you all the time, or at least I hope I can do that! Congratulations, again. Enjoy this fabulous day and all the celebrations around. Big Hugs and Kisses! Much Love, Mom.”
What a gift, an eternal gift, I thought as I read and reread the two letters. More than anything, I silently bowed in amazement, understanding how Jacquie had faced her own version of “The End.” Doug reminded me that she’d written her letters while in a wheelchair, paralyzed on one side.
With Jacquie’s example in mind, I finally sat down and read the pile of documents my lawyer had sent to me, realizing that my denial served no purpose. To my surprise, I found comfort in taking care of that necessary business — once done. I’d like to think that was something Jacquie felt, too, as she sent her missives into the future.
Complete Article ↪HERE↩!

Dan Kuester and Kirsten Farnsworth had only been married for two months when Kirsten was diagnosed with cervical cancer. Between aggressive treatments over the course of the next five years, Kirsten and Dan built a life together: they finished graduate school programs, traveled, and adopted a rescue dog they named Sputnik.
But the cancer came back in the summer of 2017, and the couple knew it was time to accept facts: At 32, Kirsten was going to enter the last phase of her life.
They decided to hire an end-of-life doula — a death doula or death midwife — to help them through the process.
“I’ll admit neither of us was incredibly familiar with the idea of an end-of-life doula,” Kuester says. “We didn’t have any kids so we had no familiarity with doulas as far as midwives go.”
The term doula is often associated with birth, a Greek term that loosely translates to a woman helping another woman. Birth doulas are trained professionals who provide mothers with emotional, physical and informational support before, during and just after birth.
Death doulas do the same, just at the end of life instead of the beginning.
Across the country, programs are cropping up that teach people how to become end-of-life doulas, holistic caregivers who support those in the process of dying (and their loved ones) with a variety of services, from practical tasks like creating a plan for the final days of a client’s life, to the psychological work of internal and external forgiveness and acceptance. This is not hospice care, but something supplemental; while hospice care keeps patients comfortable with medication, provides relief through treatments and assesses ethical medical issues with the family, death doulas are more like traveling companions, there to walk with clients and families toward something wholly unknown.
An end-of-life doula can help with cleaning or cooking, run errands or just be physically present for a client to talk to about things loved ones just aren’t ready to hear — like the reality that the end is coming.
Boulder is home to one such end-of-life doula program. Tarron Estes founded the Conscious Dying Institute after a career working as a transformational learning consultant in health care systems showed her what it looks like to die in the United States.
“When I realized [health care systems] really weren’t talking about [death], I had a very strong vision: You will change the way people are cared for in senior communities,” Estes says. “It made sense to me that if I wanted to change how death is happening in America I would do what I do best, which is work with individuals and help them experience personal transformation that also gives them a career in end-of-life care and healing.”
Through the Conscious Dying Institute, students can complete several end-of-life education programs, including a two-phase, eight-day onsite Sacred Passage Doula Certificate Program.
Nicole Matarazzo was one such student. She went on to become a doula for Kirsten Farnsworth in her last months.
Matarazzo had spent most of her professional life working directly with death; after college as a child life specialist in pediatrics working with children who were born HIV positive, then with patients receiving bone marrow transplants.
She went on to teach kindergarten and become a massage therapist, then eventually, after having children, went to work in health care at elementary schools in Boulder, where she says her role was as much about providing emotional support to kids as it was about caring for illness and injury.
About four years ago, a friend of Matarazzo’s was diagnosed with cancer for the second time, and she asked Matarazzo to care for her in her remaining days.
For a year, Matarazzo walked through the last phase of her friend’s life with her. Without question, it was emotionally the hardest work Matarazzo had ever done.
“A few hours after we had called hospice to come and be with us, [a hospice worker] asked me, ‘Where did you get your training?’” Matarazzo says. “It prompted me to wonder: ‘Why did you ask me that? How are people dying in this town?’”
The answer from the hospice worker: “Often alone and scared.”
“I heard that as a message loud and clear,” Matarazzo says. “I knew at some point I would figure out how I was going to be a player in that arena, so that there are less people dying afraid and alone.”
Trends in American lifestyles have raised the risk of dying alone: the divorce rate for 55- to 64-year-olds doubled from 1990 to 2015, according to the National Center for Family & Marriage Research, and once divorced, people are remarrying less often. One study found that nearly 7 percent of U.S. adults 55 and older had no spouse or biological children, and that number is predicted to surge over the next 50 years.
Perhaps, then, it’s no coincidence the death doula movement is flourishing.
“I think it’s been slowly beginning, quietly, kind of a grassroots movement,” says Jeri Glatter, vice president of the nonprofit International End of Life Doula Association (INELDA) based in New York City.
“I think a big part of [the rise of the deal doula movement] is the people who said in the ’80s that they did not want to give birth a certain way — that they didn’t want to be put in a white hospital and have a white male say, ‘You’ll go to sleep, and you’ll wake up, and I’ll hand you a baby’ — I think those same people are turning 70 and 80 now, and there’s an awareness that they don’t want to die the same way; they don’t want to be disconnected from what’s happening.”
Glatter, like Matarazzo, came to her work after caring for a loved one at the end of their life. The experience, somewhat counter-intuitively, filled Glatter with a “sense of joy and enlightenment.” A friend said she should consider becoming a death doula.
“I Googled the term, as per my friend’s direction, and I found the Open Center in New York City,” Glatter says. “It was the only thing listed; one Google response to ‘death doula’ [at that time].”
At the Open Center’s Art of Dying Institute program, Glatter met Henry Fersko-Weiss, a clinical social worker who created the first end-of-life doula program in the U.S. at a hospice center in New York City in 2003. Fersko-Weiss had studied the work of birth doulas, not because he was interested in becoming one, but because he saw the parallels between supporting people at the beginning of life and supporting them at the end of life. After more than a decade of moving from hospital to hospital teaching his volunteer-based end-of-life doula program, Fersko-Weiss dedicated himself fully to the cause and opened INELDA in 2015.
“Our training and our model of care has always been based in this volunteer, being-of-service format,” Glatter says.
While INELDA teaches courses on business development for those who want to professionally practice end-of-life doula work, Glatter says these courses always focus first on providing ways to make care accessible to those who need it, through sliding scale fees, pro bono work and other forms of payment that may be available to people, like trading services.
“We focus first on what brought [a student] to this work and the meaning behind the work, [their] intentions with this work,” Glatter says. “The term ‘calling’ is probably the most common term we hear from people who take training and business development courses through INELDA. We try to keep that in the forefront of the conversation. After that there is the understanding that if you are approving a service and someone is in a position and wants that support through a higher practitioner, there’s nothing wrong with being paid for that.”
In early 2017, Fersko-Weiss told USA Today that trained and certified non-volunteer end-of-life doulas typically cost between $40 and $100 per hour, with flat rates often applied during a patient’s final days so that round-the-clock care can be provided. End-stage doula services, he said, range from $1,200 to $4,000.
Glatters says that she, Fersko-Weiss and INELDA president Janie Rakow have never charged for their work.
Some doula training organizations are focused solely on training volunteers, like the nonprofit Doula Program to Accompany and Comfort in New York, which has been operating since 2001. Each year the program accepts between 13 and 15 volunteers from an application pool of 300 or so. These volunteers go into hospitals and meet with patients at least once a week through their dying phase.
To executive director Amy Levine, end-of-life doula work is about “lending our humanity.”
“We can do this for each other as human beings,” she says. “Even just 15 minutes together every week. It changes both lives.”
Nicole Matarazzo says determining appropriate payment for her services is an ongoing learning process, and she works to provide as much pro bono work as she can.
“My biggest challenge as a death doula is the exchange of money because this work to me is so sacred,” she says. “Having the conversation around what I do makes me nervous because there’s integrity and accountability around what I do.”
Becoming a certified doula can be pricey as well. The End of Life Doula Certificate offered at the Conscious Dying Institute costs $2,995 and provides nurses with 66 Continuing Education for Nurses (CNE) credits. At INELDA, it costs $750 to attend a two-day training, $100 for a current membership in INELDA, $35 to request a certification packet, and a $75 application fee, bringing the total to $960.
Currently there is no regulatory body that standardizes practices around end-of-life doula work, but most programs offer similar courses structured around providing emotional and spiritual support, assisting with unfinished business, creating visualizations, deciding how the space will look and feel at the time of death, designing rituals, developing a vigil plan and any other nonmedical gaps in care. There’s no regulatory agency for birth doulas, and most end-of-life doulas feel such an agency might limit access.
“As soon as hospice became a Medicare benefit it got whittled down year after year until it became so hard for people to get what they need,” says Tarron Estes of Boulder’s Conscious Dying Institute. “What I hope is that my work goes more and more into health care systems so that people who are on the front line can have this kind of training, so that they are supported to be who they are and they can stand for wonderful, beautiful deaths. I want CNAs to have end-of-life certifications. I want systems like Kaiser to work with me to figure out how to do a training for their employees so … more of this work can get in the minds, bodies and hearts of people that are called to do this work.”
The interest in improving end-of-life care is even beginning to infiltrate medical schools, where students are required to attend a birth, but not a death. Atul Gawande, a surgeon in Massachusetts, is leading the charge to improve education about end-of-life care at Massachusetts’ four medical schools: Harvard University, Boston University, Tufts University and the University of Massachusetts Medical School.
One thing seems certain: the need is there.
When Kirsten Farnsworth passed on May 30 of this year, her husband Dan Kuester helped his mother-in-law wash Kirsten’s body with essential oils, an ancient ritual that Nicole Matarazzo, as their doula, suggested. Kuester said that of all the planning Matarazzo helped with — visualizations, planning for the vigil and emotional support — washing the body gave him the most peace, the closest thing he can describe as “closure” on an experience that never truly ends.
“Nicole, I think partly by virtue of the fact she could come in and not be responsible for Kirsten’s physical health, it made it easier to trust her in an advisory role,” Kuester says. “She also brought a mindful and compassionate and extremely calming presence. I think both Kirsten and I felt much calmer on days when we would have meetings with Nicole, being able to plainly state what it’s like, some of these things that were in front of us that we weren’t completely sure of how it was going to go. She did a great job of showing us how it was, how these experiences were going to go and what options we have to impact the ways the experience goes.”
Death, reminds Tarron Estes, is not a medical event.
“It’s just sad because we don’t know how to be with death anymore,” she says. “Thank God we’re all beginning to think about how to do this better because none of us, myself included, people who have had the benefit of transformational work and sustainable energy and sustainable lifestyles and all the bells and whistles that a Boulder person and people who are conscious have had all their life, even most of us don’t think about it and don’t know what else there is to do. Believe me though, we’re going to be wanting to know about it.”
Complete Article ↪HERE↩!

Dr. Shoshana Ungerleider is bringing together a cross-disciplinary set of minds to reimagine what dying in America looks like today starting with palliative care in the United States. After years of seeing how the system provides less-than-desirable services to patients and their families, Ungerleider extended her career as an internist at one of the best teaching hospitals in the country to focus on awakening a global movement with the End Well Foundation.
Born just outside of Eugene, Oregon, Ungerleider never thought she would become a doctor. Majoring in science with a focus on marine biology, she very quickly realized that she preferred interacting with humans and took her career in a different direction. It was a chance internship at Duke University that sparked an interest in medicine. With the support of her mentors, she applied and completed medical school at Oregon Health & Science University in Portland.“I always knew that I wanted to be in service of other people in some way, I just didn’t know what that looked like,” Ungerleider said. “It was always very important to me. “I realized medicine was the path for me.”
Ungerleider completed her residency program at California Pacific Medical Center in San Francisco. After a rotation in the ICU, she realized that most of her patients were older, with chronic diseases and in a state that was not going to drastically improve. “Nothing that we were going to do for them was actually going to help them,” Ungerleider realized. “We were not turning back the clock on their age, we were not going to be able to cure their cancer that was widely metastatic, and we couldn’t give them a new heart.” Many of her patients were suffering and dying, hidden away from people they love, she found. And they and their families were not provided with options or a conversation about what was going on. “I realized that it’s sort of the default thing that we do in this country—no matter how old you are, no matter how sick you are, you will be admitted to an ICU, even if it won’t help you,” she said. She soon asked herself, What is the bigger picture? What is it that doctors are meant to do for patients, and are we doing that for everyone we serve?
Per a 2016 study in the Journal for American Medical Association, a peer-reviewed medical journal, 70 percent of doctors surveyed in the U.S. said they have not been trained to have difficult conversations with patients. “If communication is one of the biggest parts of the job, then how is it possible that the least amount of time is spent on exactly that,” pondered Ungerleider.
She discovered that there was a hugely under-recognized, epidemic happening in hospitals for patients to truly have human-centered care, with a lot of that being directed toward serious illness and end-of-life conversations. And, this is especially important when doctors are trained. “As physicians in training, we are often the very first people to see a patient when they come to the hospital. It’s actually possible to change the course of their treatment trajectory if physicians know how to have conversations with patients and their families based on their goals and understanding what it is that they value in their lives. Much of that doesn’t get translated into the care that they receive, and we must do something about that,” said Ungerleider.
In shifting her own conversations with patients, Ungerleider started a clinical program to train residents and medical students to have competence in palliative medicine starting with communications training. Palliative care is a field of medicine that is fairly new, a multidisciplinary, approach to medical care that is focused on quality of life for patients and their families facing terminal illnesses. Providing necessary support and comfort beyond hospice, palliative care can be used at any time during the course of an illness.
Ungerleider’s work with the hospital’s foundation inspired the inception of her own foundation, focused on bringing awareness and public engagement to the systemic change that is necessary for people to live life more fully to the very end. “I was interested in creating a shift in how society motivates people to have conversations about this topic with people they love, so that if they do end up in a situation where they are receiving medical care, the care that they get is the care that they want. I want everyone to understand their options, and how to make decisions in line with their goals and the values of how they live their lives. That, to me, is good medicine, whether we’re talking about diabetes care and high blood pressure or about the end-of-life experience,” she said. In 2014 , Ungerleider started the Ungerleider Palliative Care Education Fund to do exactly that. With the mission to further palliative care education at every level. In collaboration with the California Pacific Medical Center Foundation, the Ungerleider Fund initiated a comprehensive education program to enhance medical training around advanced illness and end of life care, physician communication and wellness for healthcare providers at Sutter Health’s California Pacific Medical Center. The foundation has financed the production of two films, both acquired by Netflix—End Game (with directors Rob Epstein and Jeffrey Friedman) and Academy-Award nominated Extremis (by director Dan Krauss) both —with the goal of educating and expanding the thinking around decision making, palliative and end-of-life care.
When asked about how her foundation became a reality, Ungerleider notes she would go to conferences around the country and meet exceptional people working in palliative care, across policy, hospice or caregiving. “They were and have been doing incredible work, yet it was always the same people. I noticed that we do a lot of ‘preaching to the choir’ in this field and don’t get outside of our traditional spheres of influence to engage other people in a conversation,” she said.
To expand the conversation beyond the medical field, in 2017, Ungerleider launched a one-day, TED-style symposium, End Well, with this very thought in mind. She asked herself, How do we create an opportunity to bring together not just those practicing palliative care but include a cross-disciplinary set of professionals working to amplify this topic through their individual work? Creating a discourse of this nature has opened up unique opportunities to bring the public and private sectors together to more deeply understand the opportunities that exist for patients.
“I feel so strongly that death and dying are not just a medical issue but a purely human issue that behooves all of us to get invested in this conversation,” Ungerleider said. ”My goal with End Well is to bring new voices into the fold, to hear from entrepreneurs who think differently about this space, to hear from patients, caregivers, artists, educators, and my fellow colleagues in medicine, too. We need to lower the barriers of entry to this conversation because we have a wide-open space to innovate new solutions: We have 10,000 baby boomers turning 65 every day in this country. It’s a looming crisis.”
As Ungerleider gears up for this year’s End Well Symposium on December 6th in San Francisco, she attributes the following elements to her success:
Listen first: “Within the first 60 seconds of meeting a patient, I can often learn more by simply listening than by talking. For patients to be engaged in their own health, they must understand their diagnosis, treatment and potential outcomes. This starts with listening to them,” she said.
Focus, focus, focus: “One of the things that my husband has instilled in me is being very goal-oriented, so I’m hyper-focused around palliative care, hospice, end-of-life—that is all that I do. My mission is to have conversations about mortality be so commonplace that I don’t need to do this work anymore, that palliative care can go away as a field because how all medicine is practiced is good medicine. That is my end goal and everything I do; I align with that goal,” she said.
Be open to opportunities: “I never imagined I’d end up running a foundation, executive producing films and starting international conferences. The opportunity to be part of the films was unexpected and it’s because I remain open and curious about how new opportunities play into advocating the work I’m doing.” Ungerleider said.
Complete Article ↪HERE↩!