The doctor helping people to die
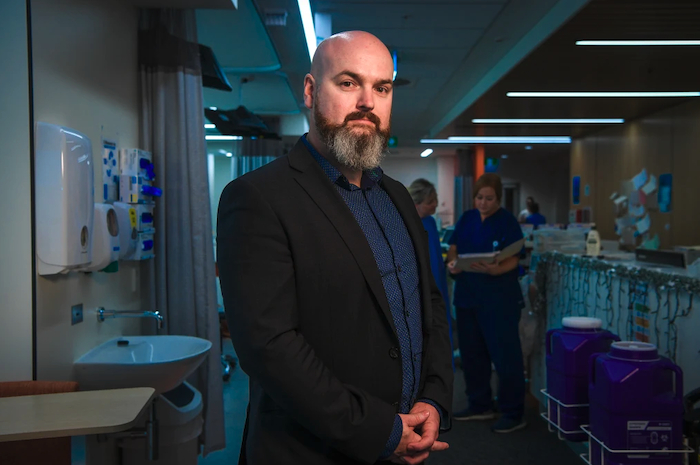

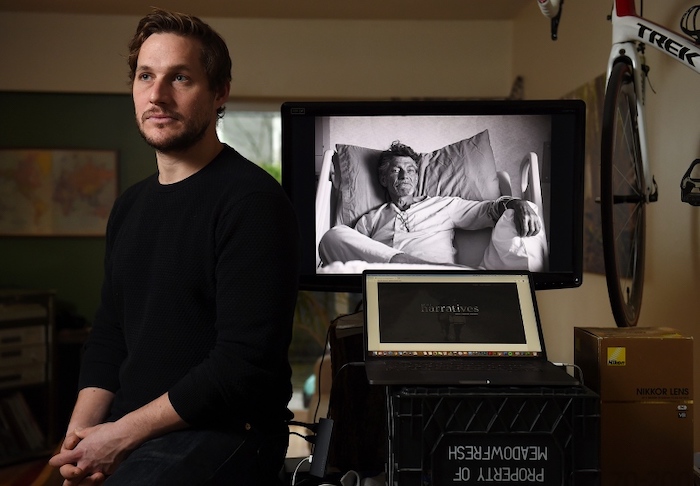
It was just after 2pm on October 31 when oncologist Cameron McLaren arrived at Phil Ferrarotto’s house on the outskirts of Melbourne to help him die.
Dr McLaren had never administered a fatal drug to a terminally ill patient before. He was struck by the magnitude of what he was about to do.
“I had no idea if I was going to be OK with it even up to the point where I put the needle to his arm,” Dr McLaren said. “But there was no question that this was the right thing to do for Phil. It was what he wanted. It was kindness and it was a mercy.”
Phil hadn’t eaten for days. No longer able to digest his medication, the 70-year-old was hooked up to an intravenous morphine drip and sustained by spoonfuls of cola-flavoured ice.
He lay in bed with his daughter Katie and wife Dorrie curled up on either side of him. They cuddled his frail body and watched his chest rise and fall with each painful breath.
His son Glen and son-in-law Ryan came into the room with three glasses of aged Glenfiddich whisky; one for each of them and one for Phil.
They toasted Phil as Dr McLaren gently swabbed the father-of-two’s arm with medicinal alcohol.

Dr McLaren found a vein and inserted a cannula. He used the thin tube to inject a sedative medication, before administering an anaesthetic and a muscle relaxant.
Phil began to drift off within minutes of the drugs flowing into his bloodstream. The circle of his family closed in around him. They held his hands and told him how much he was loved. “Be happy,” Phil said, before he took two final, deep breaths.
Dr McLaren has helped two dozen terminally ill Victorians apply for permits to end their lives since the state’s voluntary assisted dying laws came into effect on June 19. Eleven of them have since died using the legislation.
All the patients Dr McLaren has assessed so far were in intolerable pain and often bedridden.
“The number one reason people are doing this tends to be more the existential suffering,” Dr McLaren says. “It is the loss of joy, the fear of losing dignity and the fear of losing autonomy and of being a burden to family.”
Cancer-stricken patients surrender their bodies to years of treatment they know will cause them pain and discomfort, Dr McLaren said. He wants to give people control at the end of their life.
“It is one last decision about their body which is entirely theirs,” he said. “This is something we do for animals and when they get too old and they are suffering greatly. We put them out of their misery and we call it humane. Why shouldn’t we afford humans the same humanity?”
When Dr McLaren first met Phil he was sitting in an armchair in his living room hooked up to an oxygen concentrator. The cancer had spread from his bladder to his lungs and had riddled his bones. Then it invaded his liver, causing his belly to swell and fill with fluid. Opioids prescribed to Phil did little to dull his pain. Each breath was agony.
This kind, strong-willed, clever, retired general manager, who had battled four different kinds of cancers over the past 18 years, was frank and direct.
He told Dr McLaren he wanted to end his own life.
Dr McLaren carefully assessed Phil. He ticked off all the strict criteria; over the age of 18, of sound mind, an Australian citizen with less than six months to live. He referred Phil on to a second doctor who also deemed Phil eligible for the scheme.
Before his application was approved an email from Phil arrived in Dr McLaren’s inbox: “This gives me no pleasure in begging you to end my life, but I have no one else to turn to. I’m struggling with every breath I take and I can’t do it anymore.”
A permit for a doctor-administered death was approved the same day by the Voluntary Assisted Dying Board with Dr McLaren agreeing to administer the fatal dose.
For days after Phil died, Dr McLaren was waiting for the “hammer’s fall”.
“I was really concerned about the fallout for me, personally and emotionally,” he said. “I was concerned about being recognised as ‘that’ doctor and the impact it might have on my family and my work.
“I didn’t question what I did, because in Phil’s case, he was in the last days of his life and he was going to die within 48 to 72 hours. I was able to provide him a death that in his mind was dignified. It didn’t cost him anything. It cost him his suffering.”
The fallout never came.
“It was a lonely experience because there’s no literature review you can read on it,” he said. “It still does feel lonely because there’s not a lot of us doing it.”
The night Phil died, Dr McLaren picked up his two year-old daughter when he got home and held her in his arms. His love for his child overwhelmed him and he pressed his face against hers.
“As I was holding her I thought of Phil being surrounded by his family as he took his final breath,” he said.
“Nothing that we could have done would have avoided his death, but we were able to make sure Phil died at home in the arms of the people who loved him most. I thought, yeah, that would be a nice way to go.”
Before he died, Phil wrote a letter to Dr McLaren thanking him for what he was doing:
Complete Article ↪HERE↩!