Death doulas: the end-of-life guides who are recreating the dying experience
By Isabel Bird
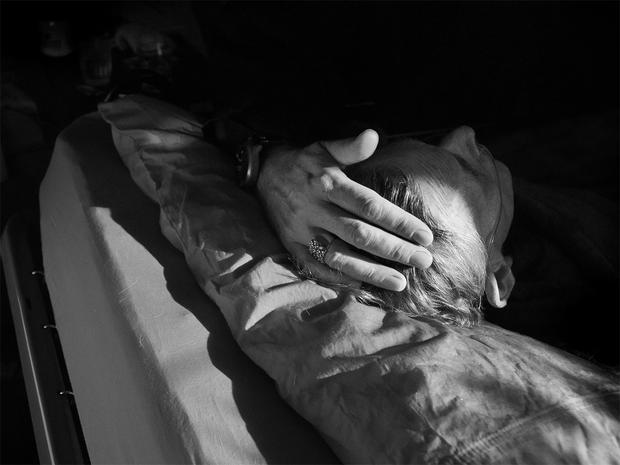
When Rebecca Lyons’ great aunt died, her body remained with the family.
Her aunt’s body was kept cool with the use of dry ice for four days, and the family washed and dressed her for service, held ritual, and prepared themselves for saying goodbye.
“We had candles, we burnt frankincense … it was a gentle process because there was no loss of ownership. It was about coming together and having that time, to laugh and cry, and it wasn’t all doom and gloom,” Ms Lyons said.
“You have looked after this person in life and now you are going to look after this person in death … the whole experience is precious.”
It was a personal death-care experience for Ms Lyons that was also connected to her new role as a death doula.
Doula in Ancient Greek translates to “woman of service” and is traditionally used in the birthing sector, but has been adopted by the death-care movement.
A death doula, end of life doula, deathwalker or death midwife can be hired by a dying person or their family to offer support in a multitude of ways, which can include organising alternatives to conventional funeral home offerings.
Their services ultimately depend on individual need and choice but can range from pre- and post-death planning, assistance with wills or advance care directives, bedside vigils, and the organisation of counselling, respite or other therapies.
Planning options may include dying at home, keeping the body at home for one day or more before burial or cremation, or holding family-led funerals in alternative spaces such as in the home, in the backyard, on a beach or in a forest.
Ms Lyons, a former funeral director, became a qualified death doula four months ago, offering the service as part of her death-care advocacy business You n Taboo.
She said a death doula helped people to make informed decisions, and then worked with families to help carry out those decisions.
“There is so much involved in the death and dying process, yet there is a lack of community knowledge about it,” Ms Lyons said.
“From the point of death a nurse might say ‘which funeral director should we call?’ The question should actually be ‘do you want a funeral director called?’ Right from the start, there is a lack of information given (in the institutional space),” she said.
“When someone dies the family can legally take the body home. Funeral directors are not mandatory, there doesn’t need to be embalming or temporary preservation, coffins are not necessary, and there are choices about the funeral and where it is held, or if they even have one.”
Ms Lyons said planning for death can be beneficial for families because it takes the guess work out of wondering what their loved ones want, and can be beneficial for the dying as they can focus on spending time with family.
Zenith Vorago is the founder of the Natural Death Care Centre in Byron Bay, which has offered deathwalker training for 12 years.
She started working with dying people 25 years ago after dissatisfaction with the conventional way of doing death, which generally involves hiring a funeral home director and relinquishing control of the body.
“We didn’t want to give our people to the medical system, or to funeral directors we didn’t know,” she said.
Ms Vorago explained that the funeral industry in Australia is led by one corporation that had a monopoly over various links in the chain, from funeral homes and crematoriums down to coffin makers.
“There is a lot of money to be made and in my experience people don’t mind paying for a service but they don’t want to get ripped off.”
Ms Vorago also said the health care system would soon not be able to cope with the ageing population, and more people in society would need to care for their own dying.
“What we are doing is skilling people up, so they can participate in that role with some awareness about how to do that well and how to do it with the system (such as) using community nurses,” she said.
“We are empowering people to know what their options are, to consider what is best for them and their people, to make decisions that are right for them, so people die well.”
Social worker Lynne Jarvis has completed Ms Vorago’s deathwalker training, and runs JUMAVE on the North-West Coast.
Her business adopts a holistic, social justice approach to death, offering a range of pre- and post-death services similar to that of a death doula, including funeral celebrancy and the use of cooling blankets for at-home funerals.
Ms Jarvis is also responsible for organising the Coffin Club at Ulverstone, where people can make their own coffins and have open, end-of-life conversations.
She said increased family involvement in the death care process can lead to highly meaningful experiences, and provided the example where an individual held a wake before their expected death.
“It ended up being really beautiful experience for them, it was well planned and simple. As sad and painful as it was, there was still beauty and joy in that process on reflection.”
Ms Jarvis stressed that early planning was important.
“I am focused on training the after-death care (family and friend) network to make sure they know what they need to do,” she said.
“It does take more energy and time … but there is great value and healing, and that healing is really important for the longer term bereavement of those left behind.”
Alternative options, such as taking the body home, will never alleviate grief but it can ease the process.
Ms Lyons said that when someone dies people often feel a loss of control, which is heightened when the body is taken away.
“It brings a massive, massive trauma that adds to the grief … what we are saying to people is that you don’t actually have to do that,” Ms Lyons said.
“For those who suit the conventional processes there are funeral directors out there who do an absolutely almighty job, but, it is a choice.”
She added that alternative options are actually a return to the old way of doing things.
“My grandmother would tell me stories where Mrs so-and-so from three doors down died, and everyone turned up with casseroles, and the body was in the lounge room. People gathered, they mourned and grieved together. The community used to own it. We are reclaiming this lost knowledge,” she said.
“Death has an amazing way of pulling people together, and the process that my family went through, looking after my great aunt – that was truly beautiful.”
Complete Article ↪HERE↩!