By
[F]or a couple of hours on Dec. 10, the Phelps family felt like Christmas came a little bit early at their home in Henderson, Kentucky.
Their two Labrador Retrievers, Lil and Pixie, had given birth to two healthy litters, with Lil having her puppies just about a week shy of Pixie. When Amanda Phelps discovered Pixie had given birth, she called her family with the news and they hurried over.
But in the time it took Amanda to run back into her house to shower and come back outside, Pixie’s puppies had disappeared. It was later discovered that the Phelps’ other dog had attacked and killed Pixie’s litter.
“I was devastated,” Amanda said. “But the worst part about it was seeing Pixie so devastated. She was crying and searching everywhere for her puppies and they were gone. ”
Amanda and the rest of her family did their best to care for the remaining litter, but also try and comfort the now grieving dog that couldn’t stop walking around their property, frantically searching for her puppies. She knew in time Pixie would heal and so would the rest of the family. But on that cold Saturday afternoon, Amanda wondered how a day that started with joy could end with so much sadness.
“It was something that didn’t make any sense,” Amanda said. “But I told myself, ‘Things happen, and things happen for a reason.’ I just didn’t know what that reason was.”
Over the next 24 hours, Amanda faced her fair share of grief and tears as she cared for Pixie and the other little newborn puppies. But the Phelpses, along with another unsuspecting family, received the miracle they didn’t know they needed thanks to the help of a stranger.
Similar circumstances, different families
Little did Amanda know, over 400 miles away in a small town in northeast Ohio, another family was grieving a similar loss on the same day.
Katie and Dan Weese, along with their three sons, of North Ridgeville, Ohio were celebrating the arrival of a new litter of English Bulldog puppies from their 3-year-old bulldog, Indy. The family took Indy to their local veterinarian’s office to have the puppies delivered by C-section. Their 6-year-old son, Dylan, shot video of the birth.
“Indy was his best friend,” Katie said. “They went everywhere together. He was counting down the days until she had her puppies.”
Indy appeared to be recovering smoothly following the surgery, and was given the all-clear to go home to care for seven new puppies.
But not long after the Weeses gathered Indy’s puppies and helped them start nursing, they realized Indy had stopped breathing.
Dan started CPR, and Katie put their children in the car to rush back over to the veterinarian’s office. Dan realized before they got to their destination that Indy was dead.
“It was just so unreal,” Katie said. “It was instantaneous. One minute we were celebrating these healthy pups, the next we’re getting ready to bury our family dog.”
But the family didn’t have much time to grieve, now that they had seven hungry puppies who were motherless. Katie drove to the local pet store to buy feeding supplies while Dan stayed home to help their three sons make sense of what had just happened.
“Later that day, Dylan doubled over with what looked like a stomach ache,” Katie said. “I asked him what was wrong, all he could say was ‘I’m just so sad.’ And that was when we realized we needed to all cry and let what happened sink in. It was therapeutic. But then we knew we had to get work, because we had our work cut out for us.”
The Weese family worked around the clock to feed the puppies, but they knew this was only the beginning of a long journey. After one round of feeding was done, they had to start preparing for the next.
Later that night, Dan posted something on their Facebook page — Red, White and Bulldogs — detailing what had happened to Indy that day. Red, White and Bulldogs also has its own blog and has a large following.
“I needed to talk about what happened,” Dan said. “I needed to write about it. Writing and talking to people is what helps me grieve the most, and I wasn’t doing it to try and draw attention to the situation, but mainly to help me process the day.”
‘It felt like fate’
Meanwhile, in Horse Cave, Kentucky, Macy Grubbs was casually scrolling through his Facebook feed, seeing what his friends and family were up to. Grubbs breeds Labrador Retrievers, and the Phelpses used one of his Labradors as the sire for both Pixie and Lil — so the Phelps family was on his mind that day, knowing that Pixie had lost all of her puppies.
Grubbs, who also grew up with English Bulldogs, follows several different breeders on his feed, including Dan and Katie Weese. He stumbled across the post Dan had made about losing Indy.
He read the post about the now orphaned bulldog puppies in Ohio and asked himself, “What if?”
“I couldn’t believe it happened on the same day, it felt like fate that I had seen it,” Grubbs said. “I knew there was a grieving dog in Henderson, and these seven motherless puppies in Ohio, and if we timed it right, we could make it work.”
Grubbs thought it over, and then sent a message to Dan.
“Hey guys I am terribly sorry to hear of your loss. I want to throw an idea your way, it may or may not help. I have a lab that gave birth yesterday and she lost her pups. She is grieving and producing milk like crazy. If you’re interested it might be worth a try. If we can help let us know,” Grubbs wrote.
Both Dan and Katie read the message and were conflicted. It sounded too good to be true, but if it worked, it could be the answer both families needed this holiday season.
“I thought, ‘This is just too crazy.’ I said to Dan, ‘This family wants to give us their dog to feed our puppies. That’s kind of weird, isnt it? And I saw they were from Kentucky, and I thought that was weird too. Why would some strangers want to come to Ohio and help us?”
From Kentucky to Ohio
Dan decided to take a leap of faith and call Grubbs. After all, what else did he have to lose?
“I remember Macy answered the phone, and I immediately calmed down after hearing his gentle, Kentucky accent,” Macy laughed. “Right off the bat, he called me brother and I knew this was a man who wanted to do something out of the kindness of his heart.”
The two men made arrangements for the families to meet the next day. Grubbs and Amanda, with Pixie in tow, made the almost seven-hour drive to Ohio to see if Pixie could help the orphaned bulldogs.
After their introductions, what happened next was what all three parties described as nothing short of a Christmas miracle.
“Pixie just laid right down and started licking and cleaning those puppies like they were her own,” Amanda said. “She knew exactly what to do.”
Katie and Dan said they had no way to predict if the plan would work. Dogs can sometimes reject their own puppies, let alone adopt a litter outside of their own, Katie said.
“I think we were all just hoping and praying that this would work,” Dan said. “We had nothing to lose but everything to gain at that point.”
And gain they did. Amanda and Grubbs left Pixie with the Weese family, where she will stay for the next four to five weeks as the puppies continue to nurse and be nurtured by Pixie.
Unexpected blessings
Pixie has settled in just fine, Katie said, and has gained some new friends of her own.
“Our boys adore her,” Katie said. “They’ll take her outside and run with her through the woods. It’s going to be hard to say goodbye when she goes back to Kentucky, but I’m predicting because of this, we’ll be getting a big dog of our own in the future.”
Amanda and the rest of her family miss Pixie, she said, and are counting down the days until she makes her trip back home to Henderson. But she knows that Pixie getting her puppies back was the best, and most unexpected, miracle she could have asked for.
“We were two families mourning in the same way, but we found a way to find some hope through what happened,” Amanda said.
Grubbs said his reasoning for reaching out to the Weese family was pure instinct, and hoped that reaching out would bring comfort to not only Pixie, but the families, too.
“One of the first things Macy said to us was what he believed, which was the part of scripture that says ‘Love thy neighbor.’ And that’s what he did, he showed us love in a way we can’t repay,’” Dan said.
The Weese family got another unexpected blessing from this journey, too. Their son Dylan was adopted, and Pixie’s adoption of their seven bulldog puppies has hit closer to home then they thought.
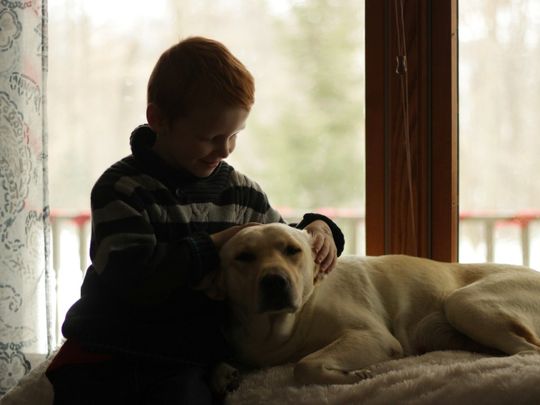

“People keep telling us this is such a great story, but the link connecting Dylan with this story has been one of the greatest blessings out of this,” Katie said. “He keeps asking us if we can adopt Pixie, because we adopted him. And even though he knows now that it doesn’t exactly work that way, I think he understands what a blessing adoption is, because he saw Pixie do it with these puppies.”
All three families agreed that they are looking forward to the exact same thing in the next couple of weeks.
“I really just can’t wait to see this yellow lab running around, with seven chubby bulldog puppies running after her,” Katie laughed. “I think that will bring a smile to anyone who sees it.”
Complete Article HERE!