An excerpt from ‘Turmeric Nation: A Passage Through India’s Tastes’ by Shylashri Shankar.

Each February, on the lunar day my father passed away, I wake up at dawn, bathe and drive over to my mother’s house. I enter the kitchen and begin sorting the vegetables. I wash the spinach and soak it in salted water. The bhindi, I pat dry. I remove the mud clinging to the arbi, rinse the green chillis, ginger and coriander leaves. Then I make a cup of tea for my mother who is unwell, and sit at the dining table to choreograph my cooking moves this year. Sixteen dishes have to be made by half past ten when the priests will arrive. Four hours to wash, chop, chiffonade, boil, cook, simmer, combine, soak, grind and fry vada, knead dough for puris, pickle the mango, roast the arbi over a low flame for half an hour, make the rice, kheer and mango chutney. Everything has to be done from scratch – no preparations can be made the previous day. Even the vegetables have to be cut on the day.
I begin the dance between the tasks like a Sufi dervish, meditatively and fluidly. These were my father’s favourite dishes – keerai, kootu, rasam, puris (we used to compete over how many puris we could eat), bhindi fry, crispy arbi with rice flour and spices, the mango and gur boiled in its own juice, and the mint chutney. These dishes were made on the tenth day after his death, and each year my mother and I make these dishes on his death anniversary. As I cook, I also think of others whom I loved who have passed away – my aunt who lived with us and was famous for her coconut barfis and chikkies, my perima who made the most delicious chutneys, pickles, papads and pastes and sent them to us from Shimoga every couple of months, my favourite uncle who was born on the same day as me and who lived a simple and contented life. I remember the things they did, and what we shared. There is a sense of calm, of peace, of unhurried movement. I salt and spice by instinct, not by taste. I cannot speak over the food, and I cannot taste it – it would be polluting. The priests arrive. After a short chant, they are ready. I serve everything course by course, on a banana leaf. They eat everything and take second helpings. I cook only occasionally, so you’d think the spices would be off, but instinct serves me well on this day. Or is it the emotions and memories infusing the cook?
Research shows that rituals can help in relieving people of their grief and other feelings that torment the spirit. A ritual, whether it is a religious one or something you have made up, helps to restore a sense of control to the mourner, control we have lost in the unexpectedness and the suddenness of the tragedy. A ritual involving cooking returns that control to you as you decide when the coriander seeds have been roasted enough, when the vegetable is done to a crunchy bite, and when the chana is cooked.
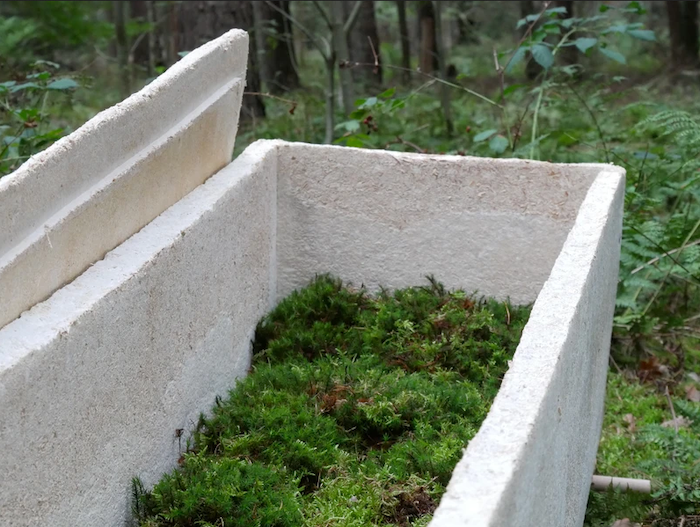
It is not surprising that many traditions contain rituals where the person who has passed on is remembered through food. The bereaved are comforted by other mourners who bring dishes like fried chicken, biryani, sandwiches and so on. The Koran, for instance, discourages the family of the dead from cooking but urges the community to bring food to the family. In Hyderabad, Muslims bring biryani, haleem, kebabs and dahi baday. Across the pond in Sri Lanka, visitors dressed in white deliver food to the mourners and the monks. The Buddhist ceremony, Daane, involves eating parupu (dal), kiri bath (rice and coconut milk) and gotu kola sambol. Pitru paksha of Hindus observed during the dark half of the lunar calendar uses food to commemorate the dead. So do similar festivals in other parts of the world: All Souls Day in Italy and Sicily where marzipan delicacies are crafted in the form of fruit and vegetables, and the Day of the Dead in Mexico where sugar skulls, candied pumpkin and mole negro are prepared for the souls of the dead.

Why are these dishes and not some others used in the formal rites? Is it because they create a sense of calm, some succour to the grief-stricken mourners? Is it ethnicity, religion or the geographic location that makes a dish or particular ingredients comforting to a mourner? In India, religion plays a key role in deciding whether vegetarian or non-vegetarian foods can be served to a mourner. Unlike Muslim and Christian mourners, Hindu mourners eat vegetarian meals even if chicken and fish are part of their daily diet. Why? It could be because death is involved in the act of eating meat (dead animals) since in Hindu culture a person is both bodily and morally what he or she eats.
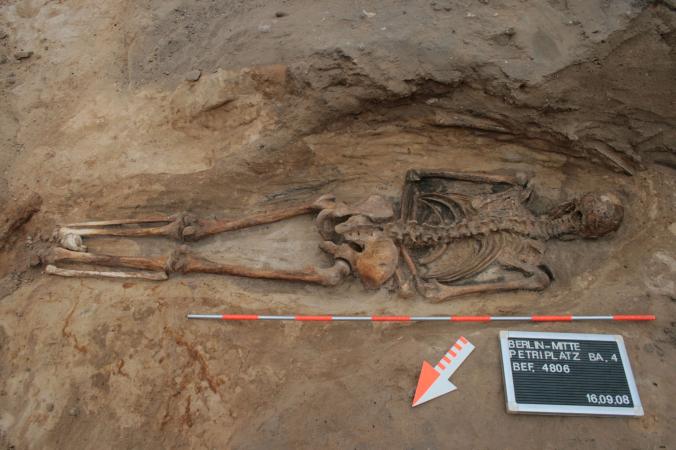
But in a study of mortuary rites in Benares, Jonathan Parry highlights how some aspect of the deceased is symbolically digested not only by the ghost but also by the ‘chief mourner, by the impure Funeral Priests (a specialist subcaste known as Mahabrahmans) and by the pure brahmans’. Parry points out that in some instances, as in the funeral rites of the Raja of Nepal, the Funeral Priest was fed the deceased’s ground-up bone in a preparation of kheer (concentrated milk and sugar), and was laden with gifts and banished from the kingdom. By digesting the deceased, his pure essence is distilled and translated by the digestive fire of the stomach to the other world, while his impure sins are eliminated. The ghost is converted into an ancestor, or pitr. The food served to the group consists of rice boiled without salt but garnished with milk and horse bean lentils (urad dal).On the thirteenth day, the mortuary feast is prepared.
Nirad Chaudhuri narrates an incident where a wealthy relative had to rubber-stamp the backs of peoples’ hands to prevent them from eating twice, many having trekked over 50 miles to attend the feast. It is not just the wealthy who have to feed hundreds of people to mark the end of mourning. The poor have to do it as well, and usually incur high debts as they sell their bullocks and grain and borrow at exorbitant rates of interest to meet the expense of feeding the village. For the Gonds and the Bhumias, the death feast is the most expensive ceremony.
The formal rites also involve other offerings in the soul’s passage from being a ghost to becoming an ancestor. Hindus offer rice or flour balls known as pindas. Some castes leave these pindas outside and hope that a crow will eat it. If it does, the ghost has become an ancestor. In Mysore, some middle castes throw three balls of butter at the idol beseeching it to open the gates of heaven (vaikuntha samaradhana).
Death need not be only of the body. The death of a relationship can be quite brutal. In mourning for the ‘we’ that has died, you may turn to your favourite dishes and binge-eat day after day. Well, don’t. In randomised trials of over 45,000 participants, London-based researchers discovered that eating meals high in vegetable and fiber and cutting back on junk food eased depression. But not anxiety. Also these meals worked better on women than men. They are trying to figure out why. NIH research has found that enhanced recovery from depressive disorders is delivered by oysters, mussels, seafood and organ meats, leafy greens, lettuce, peppers, cauliflower, cabbage, and broccoli. Now we have an Antidepressent Food Score, a nutrient profiling system to give dietary recommendations for mentally ill people.
What about foods that can increase and worsen depression? These typically are sugar-rich foods – cookies, doughnuts, red meats, fried chicken and soft drinks – that create a high followed by a crash. But dark chocolate, thank god, enhances the mood by releasing endorphins to the brain and promotes a sense of well being. I tested it over a two-week period of nibbling two slices of chocolate after lunch. Godiva’s 78 per cent cacao made me perky while Cadbury’s Crunchie left a claggy sensation in my arteries. Either there is some truth to it or I may be exhibiting the recency effect – remembering best whatever I have read or encountered most recently.
The moral of the tale is to treat grief as a natural phenomenon and address it through rituals, simple or elaborate, and eat foods that produce equanimity.
Complete Article ↪HERE↩!

 I attended my first
I attended my first