By I
“Who are you here to see?”
On this day, I was at Mount Sinai Hospital, in the oncology ward. The receptionist I usually check in with wasn’t at her desk. I was being greeted by a volunteer. Dark hair, wide eyes and a smile like a child’s doll. High school co-op student, maybe?
I handed over my health card and told her my doctor’s name.
“I’m sorry, I don’t know who she is. What are you here for?”
Her smile widens.
“Because I’m a patient?” I retort.
I know I’m being rude. But it’s an oncology ward. What does she think I’m here for? To discuss the weather? The shortage of wheelchair-accessible parking spaces in the lot?
What I really want to say is, my doctor is a palliative-care specialist. I’m seeing her because I have cancer. I’m preparing for my death.
I don’t look like I have cancer, let alone the incurable kind. I have all my hair. My friends and husband assure me my colour is good. Dressed in my normal clothes and not the pajamas I currently favour, I look reasonably well – for a middle-aged woman who also has spinal muscular atrophy, a congenital neuromuscular condition.
I rely on a motorized wheelchair to get around and need personal support workers to assist me in all aspects of daily living. It’s been this way forever, but now I have colon cancer, and two external abdominal bags to collect various bodily fluids.
This, to put it mildly, complicates things.
My palliative-care doctor is a compassionate young woman who wouldn’t look out of place in a medical drama. She has been guiding me through my own recent hospital drama: I was readmitted to hospital a couple of weeks earlier, for yet another emergency.
I’ve been fighting off a major abdominal abscess for more than a year now. At one point, my abscess was so large, one of my doctors admitted surprise that I was upright. This is what initially led to my cancer diagnosis. A colon biopsy confirmed the cancer was malignant. In October, I was told my cancer was inoperable, despite 28 rounds of radiation.
At least it’s not metastatic. Localized, but nowhere else. For now, anyway. Plus, my surgeon tells me, I likely have years with this cancer. Not months or weeks, like some of his other patients.
The challenge now is the infection associated with the abscess. During this current crisis, antibiotics are working. What my surgeon can’t tell me is when the next infection will hit, or when antibiotics may fail.
Some patients reinfect every month, he tells me. I’ve done well, he adds. I tell him I couldn’t handle being hospitalized every month. He acknowledges I would need to evaluate my quality of life, if this became my reality. In that moment, my decision to seek palliative care early seems the smartest decision I’ve made in a while.
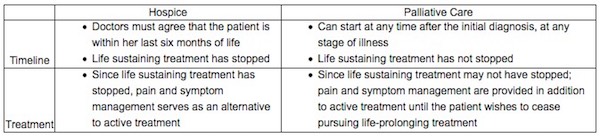
Like most Canadians, I had limited understanding of palliative care before I had cancer. To me, “palliative care” was synonymous with “you are about to die.”
That’s not the case. On my first palliative visit, the doctor explains the word is Latin for “to cloak.” She personally likes that, seeing her role as guide and protector to patients who are coping with the most difficult time of their lives.
I need her guidance. There is no clear path around how to deal with cancer while living with a disability. I’m used to being disabled. It’s my normal. My quality of life up to now has been exceptional, complete with a husband I adore, a sweet, sassy daughter and a brand-new career.
Like everyone else diagnosed with cancer, my life has suddenly imploded. I find myself in this new world, navigating how to continue while knowing the end is coming much sooner than I’d like.
That’s why I’ve sought out palliative care. My own research leads me to studies showing that having a palliative-care expert can help me prolong my quality of life through the management of symptoms, such as pain that I know will likely worsen over time. My family doctor concurs, telling me outright that I need this.
This new relationship has enabled me to talk about my greatest fears. After my conversation with my surgeon, I fear dying slowly of sepsis, waiting for my organs to fail. I’ve agreed to a Do Not Resuscitate order, which ensures I won’t be hooked up to machines in the ICU, prolonging The End.
During this particular admission to hospital and based on what my surgeon has said, my choices seem stark. Down the road, I could die slowly from an infection that will shut down my organs, or sign up for a medically assisted death.
Then, my palliative-care doctor arrives at my bedside. She points out I have bounced back from severe, acute episodes before. She also knows I don’t want an assisted death and takes the time to explain there are options available, such as palliative sedation, a process where I can have large doses of morphine to keep me comfortable. She firmly tells me I am not close to needing this. My goal needs to be focused on getting better and getting home, to my daughter.
As she explains this, I start to relax. She’s given me the window I need to live my life, as compromised as it now is. It is not the life I would have chosen, but it still has meaning. My task now is to figure out what that meaning is. And her task is to help me to define my priorities while maximizing the quality of my life with medical therapies and emotional support.
It’s an interesting time to be thinking of my life as a person who is both disabled and has cancer. Less than two years ago, the federal government enacted a new law enabling Canadians with incurable conditions, whose death is foreseeable and are suffering irremediably, to ask a doctor to end their lives.
It’s been called “dying in dignity,” but for me, that’s not the way I want to go, at the hands of a doctor, wielding a poisoned syringe.
I believe no one with a terminal illness should be forced to endure suffering – but, if there is one lesson for me in the past year, death is not the only way to alleviate suffering. Managing physical suffering feels like traveling a winding road. Some days, it feels never-ending; other days, manageable, almost like the life I had before. Some days are so bad, I’m convinced death really is the only relief, but I’m brought back to reality when I think of what I could miss out on.
My life is definitely smaller now. I doubt I will ever work full-time again. I barely leave my apartment. Thanks to my father’s financial generosity, my husband has been able to take unpaid leave from his work to be with me. The time we spend together is precious. Even in its ordinariness, it is meaningful.
I appreciate the world differently now. It is as though time has slowed for me to see the small details of life, whether it be the softness of my bed sheets or watching snow drift down through my apartment window.
I’m trying to live with dignity, as I always have, despite the very real medical indignities I have been subjected to.
Which is why it dismays me greatly there are continuing attempts to make it easier for people without terminal conditions to ask a doctor to end their life. It dismays me that a lobby organization calling itself Dying With Dignity is not actively lobbying for increased access to palliative and hospice care, or advocating for more community supports for people with disabilities to live as productively as possible. In other words, to live with dignity.
We are all going to die, but before we do, each one of us has a right to a good quality of life, even to the very end. Yet too many Canadians do not have adequate access to palliative and hospice care. The lobbying efforts of those to equalize this are rarely discussed in our media.
I’ve chosen my path, thanks to the help of empathetic doctors and my own advocacy. My hope now is that more Canadians have the right to do the same, without the implied suggestion there is only one real way to die with dignity.
Complete Article ↪HERE↩!