By Brittany Shammas & Timothy Bella
William Husel, an Ohio doctor who was accused of killing 14 patients with what prosecutors described as “wildly excessive” doses of fentanyl between 2015 and 2018, was acquitted on all counts of murder Wednesday, concluding one of the most significant murder cases of its kind against a health-care professional.
Husel, a onetime physician of the year trained at the Cleveland Clinic, faced one count of murder for each of the 14 critically ill patients he was accused of killing. The jury deliberated for seven days before finding him not guilty on all 14 counts in what was one of the largest murder trials in Ohio history.
He had been charged with causing or hastening their deaths amid a period of lax oversight of fentanyl at Mount Carmel West, a Catholic hospital in Columbus. Husel would have faced life in prison with just one guilty verdict.
While the synthetic opioid is significantly more powerful than morphine and has wreaked havoc on American streets, it can provide pain relief in medical settings that is crucial to end-of-life care. The alleged victims in the Ohio case suffered critical medical conditions including overdoses, cancer, strokes and internal bleeding. Prosecutors acknowledged that all were being kept alive on ventilators and that many of them were dying.
“In truth, William Husel was an innocent man, and thank goodness the justice system prevailed,” Jose Baez, one of Husel’s defense attorneys, told reporters.
The 46-year-old’s acquittal came after a two-month trial that triggered a debate on end-of-life medical care. Husel and Baez argued in the trial that the doctor offered comfort care for dying patients and was not trying to kill them. They pointed out that the doctor’s actions did not occur in secret — nurses were the ones to administer the doses — and alleged that hospital officials made Husel the villain after realizing the systemic failures at play. The fallout over the allegations at Mount Carmel West had repercussions: the firing of 23 employees; the resignation of the hospital’s chief executive, chief clinical officer and chief pharmacy officer; and Medicare and Medicaid funding for the institution was put in jeopardy.
But Franklin County prosecutors alleged that Husel gave patients amounts of the opioid far beyond the norm. He ordered 1,000 micrograms of fentanyl for multiple patients — about 10 times the recommended dosage, according to prosecutors. One of the patients, 82-year-old Melissa Penix, was given 2,000 micrograms of fentanyl — 20 vials of it, all at once. The amount of fentanyl given to her, which was about 20 times the recommended dosage, depleted the entire supply of the medication available in the ICU that night, Franklin County Assistant Prosecutor David Zeyen told jurors.
Joel Zivot, an associate professor of anesthesiology and surgery at Emory University and the sole witness called by Husel’s defense, told The Washington Post that he was relieved the jury determined that disease, not fentanyl, caused the 14 deaths.
“Physicians intend to provide comfort at the end of a person’s life, and the idea that the intent was murder simply by the action by giving someone pain control was unprecedented and ultimately shown to be a false accusation,” Zivot said.
The Franklin County Prosecutor’s Office released a statement commending the prosecution and defense for their work, adding that the office accepted the jury’s finding Husel not guilty.
“The Jury after review of all the evidence was not convinced beyond a reasonable doubt that William Husel was guilty of any charges submitted to them,” the prosecutor’s office said in a statement. “We accept the jury verdict.”
The case came to light in the fall of 2018 when, Mount Carmel West has said, pharmacists voiced concerns about doses ordered by Husel, an anesthesiologist who had been employed at the hospital about five years and worked on the skeleton crew of overnight intensive care. He was well liked in the ICU and known for his willingness to teach those who worked alongside him.
In total, at least 35 people may have been given excessive doses, the hospital said after a review. All of them died; the hospital said five might have had a chance to improve. Officials alerted police, and Husel was charged in June 2019 with 25 counts of murder. Prosecutors dropped 11 of the charges.
During closing arguments in the trial this month, Zeyen argued that even if the patients were dying and Husel thought he was acting in their best interest, killing them still constitutes as a crime.
“That is what you do to sick animals. That’s fine in veterinary science,” Zeyen said. “That is not fine in the ICU at Mount Carmel.”
Baez responded by referring to Husel’s pledging to provide comfort to the patients, noting that the doctor had much to lose.
“Why would this man risk his family, his career, 17 years of trying to be a doctor, every single thing he has worked for, to hasten someone’s death or to kill them?” Baez asked during closing arguments.
Zivot told The Post that he reviewed each of the cases and concluded that Husel offered the kind of care that any doctor would have provided for end-of-life treatment.
“Dr. Husel did the thing that doctors do in that he provided some fentanyl for the purpose of mitigating what we imagine to be the pain of dying, and that’s it,” he said. “We cannot know what it feels like to die; we can only imagine it. We fear it, and we are concerned about that. If we can’t stop someone from dying, at least we can reduce the pain associated with dying.”
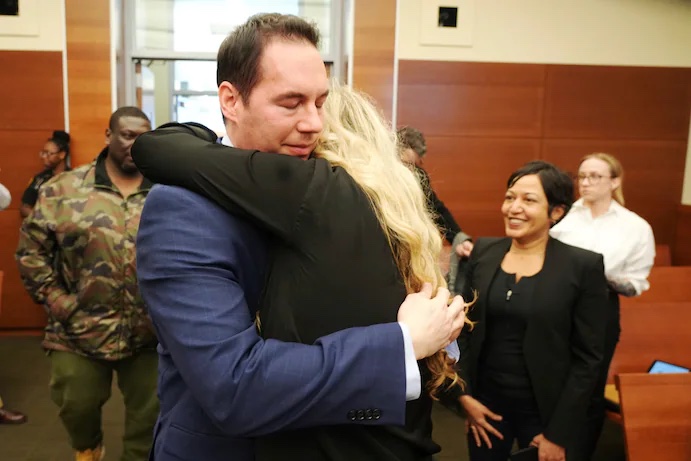
When Common Pleas Court Judge Michael Holbrook read each verdict of not guilty, Husel’s wife, Mariah Baird, watched and smiled before hugging her sister, reported the Columbus Dispatch. After all 14 counts came back as not guilty, Husel wiped away tears.
Even with his acquittal in the murder trial, Husel still faces more than 10 lawsuits from the families of patients. Several of the families have settled lawsuits worth about $13.5 million, according to NBC News.
Baez emphasized to reporters that he felt “terrible for all of the patients’ families suffering again.” But, he said, he hoped they took comfort knowing that a jury concluded that it was their loved ones’ critical illnesses, and not the opioid, that resulted in their deaths.
“Hopefully they take solace that their loved ones’ last moments were in peace and not as a result of a doctor being afraid to make them comfortable,” he said
Complete Article ↪HERE↩!