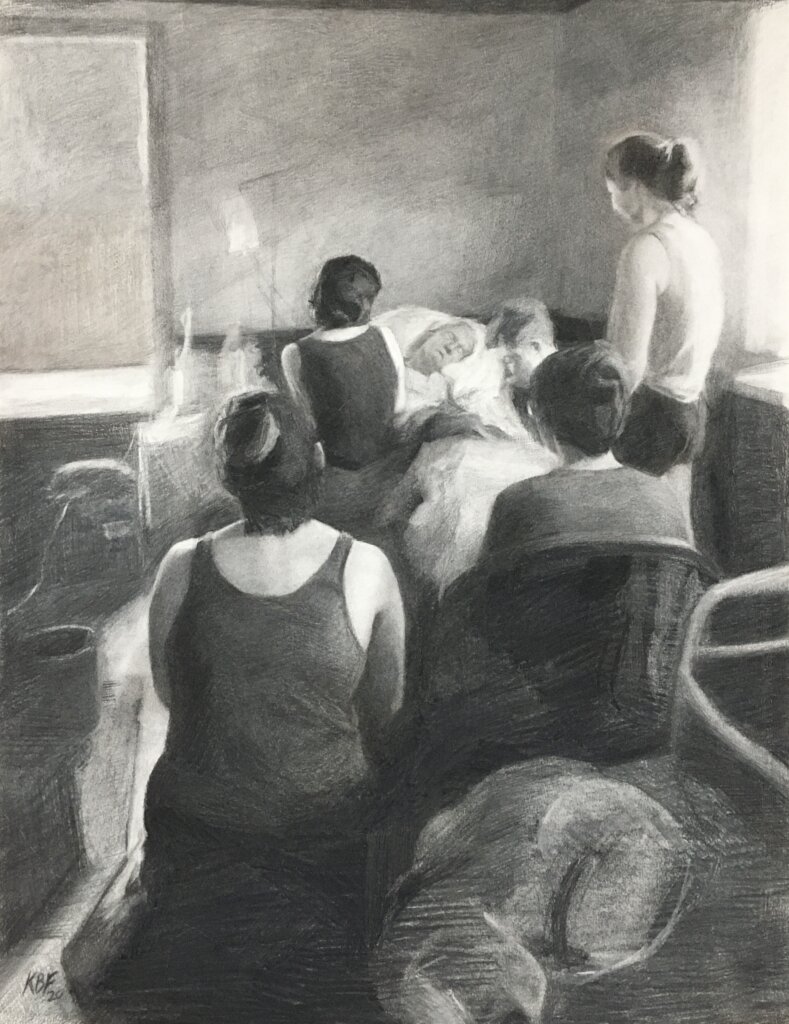— There is something quite moving about all this grief amongst all this routine.

By Hannah Davis
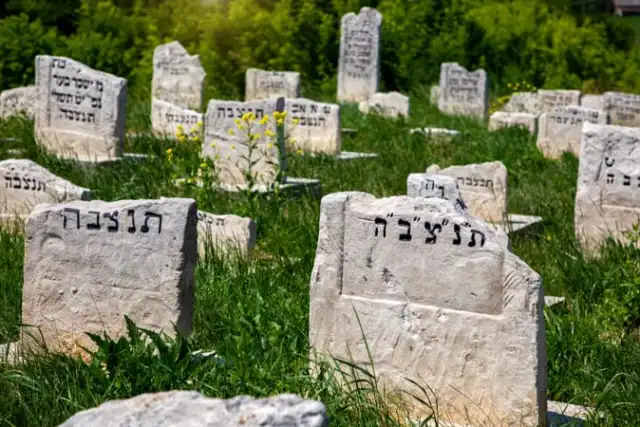
It was only relatively recently that I learned that holding funerals within 24 hours was a Jewish custom, and not the general norm. I’ve been extremely lucky in having gone to quite few funerals, and almost all of these have been those of Jewish family members, so it simply didn’t occur to me that we might be doing anything unusual in having them so quickly. Without the understanding that this wasn’t standard practice, I didn’t consider it exceptional — but the impact it has on the process of mourning can be, in my opinion, a significant and unifying one.
In the Torah, we are told that “You shall bury him the same day. His body should not remain all night.” And traditionally, the urgency of the funeral is linked to the importance of returning the body to the earth and allowing the soul to return to God. As a culturally-not-religiously Jewish person, I was unaware of both the scriptural and spiritual reasoning until very recently. I would have placed the emphasis on the emotional reasoning, which argues that the immediate experience of loss, mourning and proximity to death is a deep pain to feel, and one which should not be undergone any longer than absolutely necessary. Now it seems clear to me that it’s more about custom than anything else. Either way, I have come to hold it as an immensely important, beautiful aspect of the Jewish culture around death.
In December, my great-great auntie Marjorie became quite ill and we as a family braced ourselves for an upcoming funeral. She, along with much of my family, lived in Manchester, so in the lead-up to her passing, the London sect of us were on slight tenterhooks in anticipation of journeying up on little notice. In these moments, the banal and the profound are forced to find some kind of harmony. When contemplating loss is simply too vast, logistics take on a special importance.
In some ways, the knowledge that you’re just waiting for a death to occur so that the chain of events can start to unfold can be quite tiring. Maintaining a state of urgency over an extended period of time is logistically and emotionally tricky, and having to be pragmatic in the face of something so sad can feel like an unnecessary added encumbrance. But ultimately, there is no actively good time for a funeral. No one is looking at their diary and finding the perfect date to dedicate to doing something none of us want to do. In some ways, recognizing that the funeral will be hard no matter what, and then allowing it to take precedence over all other commitments, is the best way to allow a loss the appropriate space it deserves in our lives.
When the day arrived, a large portion of it for me was taken up by travel. We woke up to cancelled trains — standard — and then huddled alongside however many other disgruntled passengers at Euston. My mum’s cousin Caroline and I ran at absolute breakneck pace through crowds of people to get seats as soon as the platform was announced. On the drive from the station to the cemetery, we passed innumerable family monuments: the prison to which my uncle was told his parents had been sent in a prank by his cousin, the sandhills where Caroline reported “practically torturing” my mum when they were little, the shop to which it was a very grown up privilege to be allowed to walk to alone. Despite most of my visits to Manchester now being for funerals, the city will always feel full of life. Our memories and our history are part of the fabric of the place, and so many of those who we’ve lost are kept alive in the stories we can’t help but keep telling.
The funeral itself was brief and beautiful. My great-great aunt was a truly incredible person whose innate kindness and protectiveness distinguished her as remarkable to everyone around her. With it all having to come together so quickly, the words people choose take on a special significance: they are candid, and emotional, and cut straight to the core.
And yet, alongside mourning and meaning exists the mundane. People keep being people, and we continue to have to get ourselves from A to B. On the journey back to the station after the funeral, I sat squashed between my uncle and my grandfather in the backseat of my great uncle’s car, and we sat for a short eternity in a gridlock outside my grandma’s primary school, entertained by stories about that time of her life. When we finally got to the station, we caught a train by the skin of our teeth. By holding funerals so quickly, we force our lives to fit into the space around them, and require them to find a way to enmesh themselves into the day to day. There is something quite moving about all this grief amongst all this routine.
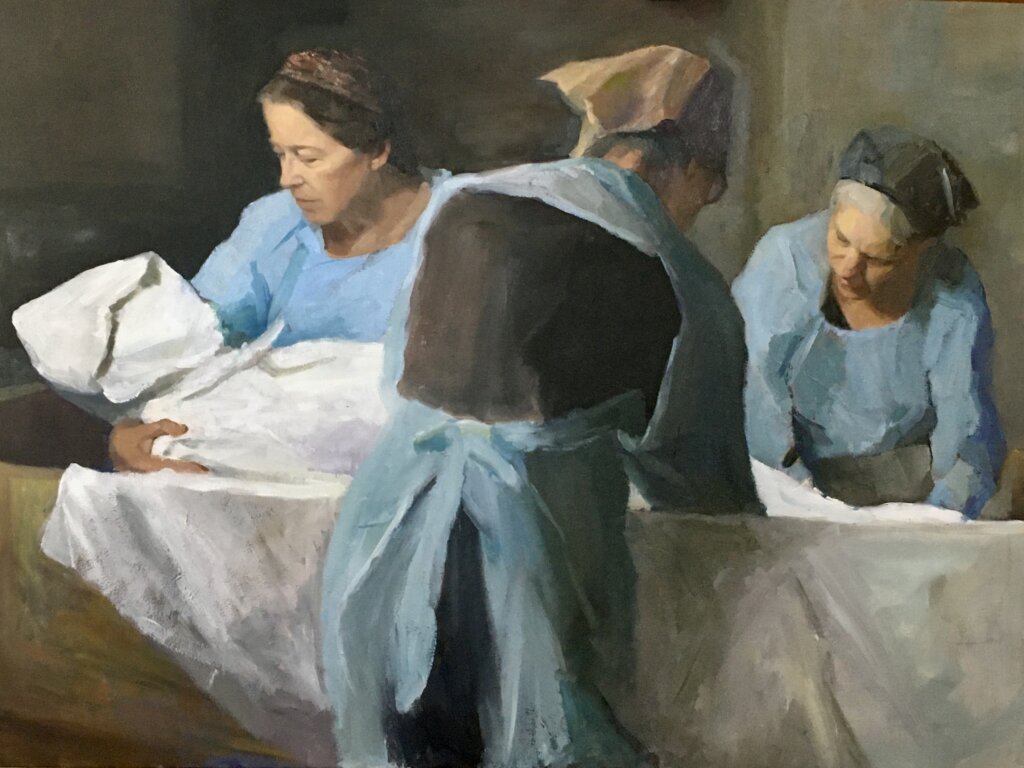
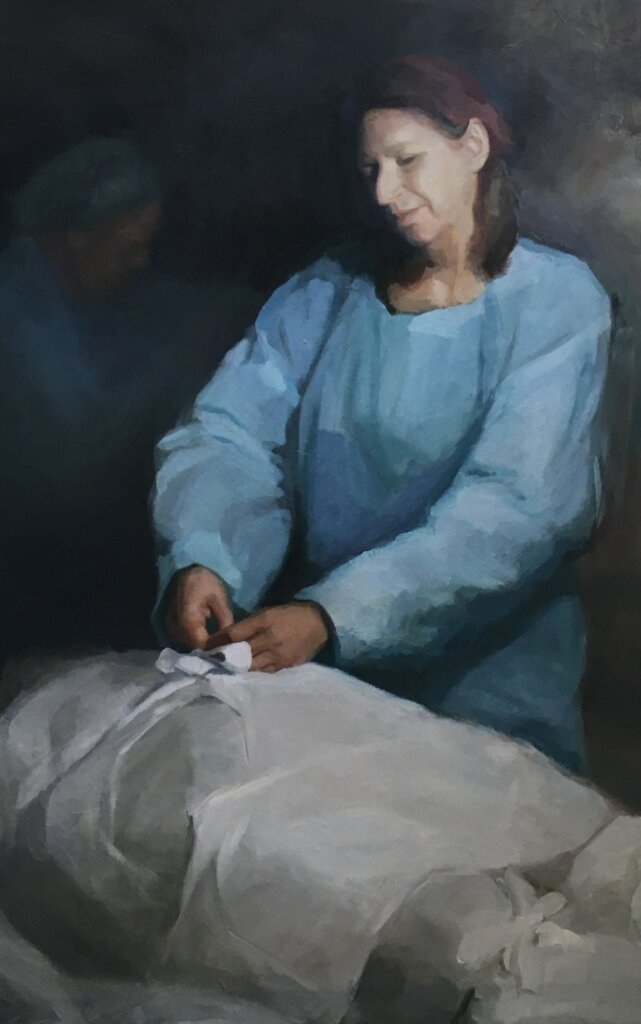
Sitting on trains gives you the wonderful gift of time to think. I reflected on my privileged position, experiencing the funeral of someone so beloved as a peripheral mourner, and how this offered another insight into the magic of having a funeral within 24 hours of a death. With this custom, in the direct aftermath of losing someone the people closest to the deceased are immediately wrapped in love. Their family and friends flock to them and make sure they aren’t alone with their grief. The initial experience of living without someone involves being in a room full of people who are there to remember and celebrate them. A funeral within 24 hours catches you just as you fall into the abyss.
And whilst there are undeniable impracticalities, the system manages to account for most. For those who are unable to make it, attending a shiva in the coming days offers them another chance to support and commemorate and mourn for themselves, as well as to contribute to the elongation of the period in which those closest to the deceased are surrounded by care. Whilst the funeral comes quickly, this does not mark the end of the grieving process — rather, it’s the beginning of the talking, processing and feeling. I am grateful that, thanks to Jewish custom, that beginning starts within 24 hours of a death. It’s exactly what we need.
Complete Article ↪HERE↩!