By Katie Roiphe
Nothing informed the writer’s work so much as his abiding fascination with mortality and menace.
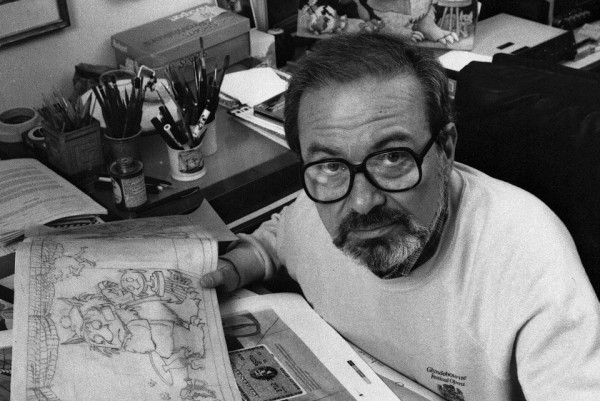

Maurice Sendak had always been obsessed with death. He drew through his obsession, used it. He drew lions that would swallow you; he drew wild things that gnashed their terrible teeth; he drew faceless hooded goblins stealing babies out of a window; he drew fat bakers who’d bake you up in a pie; he drew a 9-year-old pig that promised he would never turn 10. He drew funny, charming, cheerful, haunting near-deaths. He drew narrow escapes, popping up, resurrection.
He knew what it was like to be so depressed that dying did not seem crazy or outlandish or remote. He had a kind of intimacy with death, with the idea of it, anyway.
Even as a tiny child in Brooklyn, Maurice was unusually alert to the prospect of dying. He was floored by every childhood sickness—measles, scarlet fever, double pneumonia. “My parents were not discreet,” he said. “They always thought I was going to die.” He laid out the toy soldiers on the blankets of his sickbed. He watched other children play through the window.
One day his grandmother, who had emigrated from the shtetls outside Warsaw, dressed him in a white suit, white shirt, white tights, white shoes, and took him out to the stoop to sit with her. The idea was that the angel of death would pass over them and think that he was already an angel and there was no need to snatch him from his family.
During one illness Maurice had as a toddler, his mother found him clawing a photo of his grandfather that hung above the bed; he was speaking Yiddish, even though he only knew English. She thought a dybbuk was trying to claim him from beyond the grave, so she tore up the photograph. She said she burned it, but years later Maurice found the torn-up pieces in a Ziploc bag among her possessions. He had a restorer put it back together and he kept it in his house, this grandfather calling him to the grave.
The general message from his family seemed to be that he should be grateful to be alive, that his continued existence involved some aspect of luck that should not, if he was smart, be pushed. When he was very small, his parents told him that when his mother was pregnant they went to the pharmacy and bought all kinds of toxic substances to induce a miscarriage, and his father tried pushing her off a ladder. They hadn’t wanted a third child. Why would they tell a tiny child this? As a famous artist, later in life, he brushed the question off in an interview, as though it wasn’t in fact a big deal—they were harried immigrants, they didn’t need another mouth to feed, though surely something deeper was etched into his sense of himself. He was unwanted, unwelcome, somehow meant to die, meant to be carried off. He said once, “I felt certain my mother did not like me.”
There is a formal photograph of his dumpling-shaped mother, her wavy hair chin length, with her three wary children, the wariest of all being baby Maurice, who is dressed in a white bonnet and appears from his scowl to already be seeing some pretty wild things. She is looking at the camera as if it might at any moment leap out and attack her. Theirs was not a happy or relaxing home. Sadie Sendak was often furious. She had trouble with warmth. The siblings turned to one another, sometimes sleeping together like kittens, three in a bed. Maurice, who struggled in public interviews to be generous to his mother, said that she should never have had children, and distant, absent, prickly, punishing mothers would be a big obsession of his books.
The literary critic Stephen Greenblatt once wrote about Sendak’s books: “Love often takes the form of menace, and safe havens are reached, if they are reached at all, only after terrifying adventures.”
All his life Maurice bristled at the idea of childhood innocence and at those who thought his books were offending or challenging it. In a comic Art Spiegelman did in The New Yorker of a conversation they had in the woods, Maurice says: “People say, ‘Oh, Mr. Sendak. I wish I were in touch with my childhood self, like you!’ As if it were all quaint and succulent, like Peter Pan. Childhood is cannibals and psychotics vomiting in your mouth! … In reality, childhood is deep and rich … I remember my own childhood vividly … I knew terrible things … but I knew I mustn’t let adults know I knew … it would scare them.”
Maurice liked to tell the story of the daughter of a friend who was at school near the World Trade Center when the towers fell. She told her father that she saw butterflies on the building as the towers collapsed. Later she admitted that they weren’t butterflies, they were people jumping, but she didn’t want to upset her father by letting him know that she knew. Children protect their parents, which is the funny part of childhood that slips away from us, the awful knowledge it contains.
The received wisdom is that it is not good to scare kids, but Sendak’s belief was that kids are already scared, that what they crave is seeing their anxieties thrillingly laid out. Much of Sendak’s work, then, exists between play and terror, that infinitely intriguing, purely fantastical place where you are joked out of your most serious fears. But those fears are also entertained on the most serious and high level in Sendak’s books; they are not dismissed but reveled in, romped through.
After the runaway success of Where the Wild Things Are, Maurice ran into a friend from Lafayette High School. She was the girl he sat next to in art class. On his high-school yearbook page, which was captioned, “Your delightful drawings make us all gay. A famous artist you’ll be someday,” he had scrawled to her, “Lotsa luck to a swell gal. Sendak.”
Now she said to him, “How does it feel to be famous?” He said, “I still have to die.”
Maurice had a passion for ritual. He liked to eat the same breakfast every day—marmalade, English muffin, tea—from 9 to 11, then he would work, then get dressed and walk the dog, then have lunch, then work, then dinner with cake, and then, from about 10 to 2 in the morning, more work. The day was about creating a carapace for the work. In a letter to a reader with whom he warmly corresponded for decades, he once wrote that life was good when he was working or getting ready to work.
What is unsaid here is that life is not happy when he is not working. Like his mother and brother, Maurice had always wrangled with depression. The black moods would descend, and he would fight them off with work or, when he couldn’t work, with the idea of work. The work was, among other things, a mood stabilizer. It kept him going; it lured and cajoled him back to life.
Sendak often talked about his books as a “battleground” or “battles.” In the hours in his studio, under the cheap white lamp clipped to his drawing desk, he was fighting. The business of creating children’s books was not a sweet, civilized occupation; it was violent, bloody. He was defending or protecting himself.
“I’m totally crazy, I know that,” he once said. “I don’t say that to be a smartass, but I know that that’s the very essence of what makes my work good.” The craziness was in his work. The blackness was vital; he called it “the shadows.” The shadows were in the illustrations. Without them, there would be only charm.
Those close to him sometimes heard the extremes of depression in his voice; he had more than a passing acquaintance with the edge. He smuggled moments of numbed depression into Higglety Pigglety Pop!—“The lion said, ‘Please eat me up. There is nothing more to life’”—and into My Brother’s Book.
Maurice wrote a letter in the mid-’70s about being in a funk in San Francisco. He is working on a book that he thinks may be his finest. This makes all the difference to his mood. He talks about the book as if it has entered the world to redeem him. He knows that the idea of art rescuing you is a cliché, but in this case, it’s really true. He’s going to make it because of the book.
This seems not an overstatement: The books and drawings and opera backdrops came to save him. Or he dreamed and labored to save himself.
“Please don’t go. We’ll eat you up, we love you so!” say the wild things to Max in one of Sendak’s most immortal lines. Love here is terrifying, consuming, exhilarating; it is infinitely recognizable, even to small children, annihilating, seductive. It’s the purest expression we have of the delirious violence of strong feeling. The British psychoanalyst Donald Winnicott once wrote that the mother must resist making love to or eating her child, which resonates because certain loves are so fierce and urgent, it feels as if you want to bite or eat or consume the object of that love.
Maurice said he dreamed up the idea of the wild things as an adult, at a shiva after someone had died, with his brother and sister. They were sitting around, laughing about their relatives from Europe. The relatives didn’t speak English. Their teeth were yellow. They grabbed the children’s cheeks. It was like they would gobble up Maurice and his siblings, along with everything else in the house. The wild things were Jewish relatives.
In fact, Sendak’s books are filled with beasts that might eat you, often lions. There is the lion in Higglety Pigglety Pop!, a stately yet cryptic menace, who closes his jaws around Jennie’s head; there is the lion in the nutshell library, who swallows Pierre and then, after being hit on the head with a folding chair and shaken up and down by a doctor, spits him out again on the floor; there is the bear in My Brother’s Book, who bites the brother and kills him. The idea of being consumed by an animal is a code for death—that is, depending on the moment in Sendak’s life, either easily reversible or not. He is playing here with a very basic primal fear—being swallowed by a beast, a child’s fear—but it is also a fear of being consumed, obliterated; it is about the loss of self on the most grave and terrifying adult level. Can you be close to another person without being consumed?
He liked to say that when his sister gave him his first book, he bit it. This fits with his sensual apprehension of the universe, his physical devouring of people, places; he took things in more sensually than most—he hugged his friends, grabbed their noses, kissed them on the lips.
There is a moment in Where the Wild Things Are when Max gets lonely with the wild things, in his tent, in the great orange dusk, and wants to go where someone loves him best of all. For Max, that someone is his mother, who has made him a warm supper with a big slice of layer cake. She is one of the great reassuring presences of a mother in literature, but for Maurice, that person was never his mother. Did people love him best of all? He voraciously hungered to know that they did.
* * *
Maurice liked to watch medical shows. He would be happy sitting at the dinner table, watching a graphic reality-TV surgery show while eating spaghetti. Someone sitting with him might wonder why he liked watching a human body ripped open, what he wanted to see.
On some level this could be seen as research, as Sendak belaboring a problem that obsessed him. He had always worked extraordinarily hard. He did more drafts, more dummy books, more tracings over light boxes, more fully realized drawings for his opera backdrops than he needed to, than other artists would, than necessity demanded; he labored toward the final version; he fought for it. His mastery of so many different styles and his vast strides in technical achievement are not a mystery: He worked insanely hard for them, and he was also working, in his own vivid way, on death.
Tony Kushner wrote about a conversation he had with Maurice:
I tell him I will visit him in Connecticut. “Great,” he says. “We can dance a kazatzkah!” “What kind of dance is that?” I ask. “A kazatzkah is the Dance of Death,” he tells me. “Sounds good. Do you know the steps?” I ask. “Do I know them,” he says with glee, making a kazatzkah sound like the most fun imaginable, “I know those steps in every notch, every noodle, every nerve cell! Of course I know them! I’ve been rehearsing them all my life!”
Sendak had collected a series of beloved objects that dealt with death: Mozart’s letter to his father telling him that his mother was dead. A Chagall funeral scene. A grief-struck letter he wrote at 16 to his future self on the day Franklin Delano Roosevelt died, full of lavish adolescent sorrow, railing against the people who just chattered and laughed as if nothing had happened. Wilhelm Grimm’s letter “Dear Mili,” to a child whose mother had died.
These objects were soaked in meaning for him. It was as if he had traveled somewhere and brought home souvenirs.
Maybe the most startling of these objects is Keats’s original death mask. Maurice did not keep the wooden box containing it in his bedroom but in the blue guest room. He liked to open it and stroke the smooth white forehead. He said it did not make him feel sad, it made him feel maternal.
Maurice drew his partner Eugene after he died, as he had drawn his family members when they were dying. The moment is one he was compelled to capture, pin down, understand, see. Where many— maybe most—people look away, he wanted to render. He was very wrapped up in the goodbye, the flight, the loss; it was almost Victorian, to be so deeply entranced with the moment of death, the instinct to preserve or document it. It’s also the artist’s impulse: to turn something terrible into art, to take something you are terrified of and heartbroken by and make it into something else. For the time it takes to draw what is in front of you, you are not helpless or a bystander or bereft: You are doing your job.
He wrote another beautiful letter to a reader in 1964. He tells the story of visiting an old family friend who was dying. He was very afraid of seeing her, afraid of how his parents would feel, and afraid of how he would feel. This was the last time he would see her. And yet when he did it was strangely lovely. It was like staring into something he had always been terrified of, and it was exquisite. He left feeling both miserable and elated.
This seems to be key: Staring into something you have always been terrified of and finding it beautiful.
Complete Article HERE!