The new breed of inspirational carers helping to ensure people’s dying days are spent in the comfort of their own homes
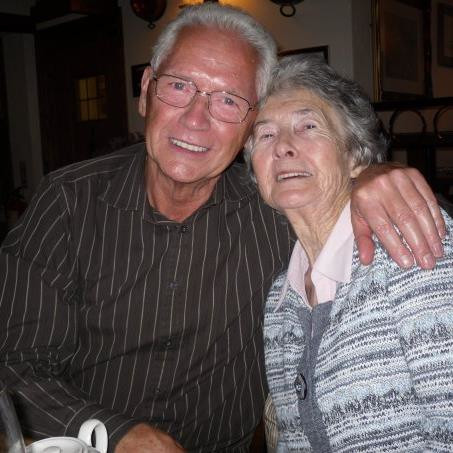
[C]olin Barber takes great comfort in the fact that his terminally ill wife, Valerie, was able to die peacefully in her own bed.
On Tuesday, September 1, 2015, ten days after she had been discharged from hospital, Valerie, who had bile duct cancer, took her last breath at home in their bedroom — ‘exactly as she had wanted, with her father and me on each side of her bed, gently holding her hands’, recalls Colin, 56, a business psychologist.
It was, he says, as serene a death as it could have been.
Yet it was nearly so very different. Instead of spending her last few days in peace at home, Valerie, like many patients, could have ended up being rushed to hospital and dying on an anonymous, noisy ward.
But she was one of the lucky ones: she was able to plan for her last days and ensure her wishes were adhered to, thanks to an award-winning new approach to end-of-life care known as soul midwifery.
The idea is that, just as a birth midwife helps to ease a baby’s entry into the world, a ‘soul midwife’ eases people’s dying days.
It is a cruel failure of modern medicine that while the vast majority of people — eight out of ten, according to the Office for National Statistics — want to die at home with their symptoms controlled and their loved ones around them, nearly half actually die in hospitals. Only one in five gets to die at home.
And just how ghastly dying in hospital can be was set out in a report by the British Medical Association published last March.
Based on interviews with more than 500 doctors and patients, it painted a grim picture of patients being given ‘entirely inappropriate invasive treatments’, and junior doctors often too fearful to provide adequate pain control.
Pressure on beds can mean dying patients are ‘shuffled between wards’, preventing continuity of care, while single rooms are prioritised for patients who pose an infection risk, so the dying rarely get privacy. The NHS failure to provide a dignified, peaceful death was highlighted this month by a study published in the BMJ’s Palliative and Supportive Care journal, which identified a postcode lottery in specialist palliative care.
As a result of this, patients are far more likely to be rushed to A&E at the end of their lives than to die pain-free, in peace, at home.
NURSES HAVE NO TIME TO CARE
The BMJ report followed a recent survey of almost 1,000 hospital nurses in which two thirds revealed they didn’t have enough time to care properly for dying patients.
Such is the concern that patients are being failed, that last week the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) re-published guidance on end-of-life care first issued to doctors in 2015.
This restated four essentials: the need for doctors to draw up a care plan, provide individualised symptom control, monitor patients daily and ensure adequate hydration. Most people, says Professor Gillian Leng, deputy chief executive of NICE, receive good end-of-life care ‘but this isn’t always the case’.

Good care involves asking people about their preferences as well as controlling pain, adds Sam Ahmedzai, a retired professor of palliative care who worked on the latest NICE guidance.
Yet a recent study showed that only one person in seven who could communicate their desires had those wishes documented.
This is far from a new problem. Ten years ago, a major report, the End of Life Care Strategy, featured an innovative plan to end the situation where ‘most people would prefer to die at home while only a minority manage to do so’, as then Health Secretary Alan Johnson put it.
Along with improved palliative care, the plan involved healthcare practitioners working harder to ‘identify people approaching the end of life and discuss with them their needs and preferences’.
DOCTORS CAGEY ABOUT THE TRUTH
Ten years on, although there has been a slight improvement (back then nearly six out of ten people were dying in hospital) there is still ‘a long way to go’, Claire Henry, chief executive of the National Council for Palliative Care, told Good Health this week.
So why is it still proving so difficult to get things right?
‘Some deaths happen suddenly, out of the blue, while with some patients it’s difficult to be sure whether they are dying or will recover,’ says Professor Ahmedzai.
‘That’s why we say that every patient in the last days of life should be monitored daily in case there have been changes and there is a chance of recovery.’
Research shows that, in fact, in four out of five cases GPs can predict which of their patients will die within the next 12 months. And three out of four deaths are anticipated by medical teams, according to NICE.
Professor Ahmedzai says: ‘We should be asking anyone admitted to hospital with a serious illness about their preferences for where and how they wish to die, should that look likely. But doctors often don’t because they are embarrassed or just too busy to handle that conversation. It can’t be an excuse. We must make time for the dying.’
Indeed, a major problem is that too often, dying patients simply are not told what their doctors know. Sometimes this is because doctors are unwilling to discharge patients so they can die at home because effectively ‘such a decision can be seen as an acceptance of failure’, the recent BMA report noted.
Certainly, no one told Valerie or Colin that she was dying.
The banking relationship manager from Brentwood, Essex, had cancer diagnosed in 2013, two weeks after her 50th birthday, after noticing that the whites of her eyes were yellow.
Her GP referred her for an MRI scan, which revealed a large tumour wrapped around her bile duct.
She had surgery to remove part of her liver along with the gall bladder and bile duct, followed by three months of chemotherapy.
‘After the treatment we began to be optimistic that she was recovering,’ says Colin. But in October 2014 a scan identified nodules of cancer in the liver, too scattered to be removed surgically. In August 2015, Valerie took a sudden turn for the worse and had to be admitted to hospital.
‘We’d just come back from holiday, when she’d canoed 15 miles down the River Severn,’ recalls Colin. ‘Then one day she woke up so weak she could barely stand.’
Even so, ‘it didn’t occur to me that she was gravely ill,’ he recalls. ‘No one at the hospital mentioned the word ‘dying’.’
Valerie’s discharge from hospital three days later depended only on a physiotherapist checking that she could walk upstairs, which the couple took to mean she was on the mend.
‘But looking back on it, her doctors must have been aware that she was dying,’ says Colin. Not least because the next day, after an appointment with the cancer specialist, she was referred to hospice care.
It was not her doctors but Valerie herself who first put what was imminent into words. ‘Back at home, Valerie told me she was dying and I had to accept it,’ recalls Colin. That was when she asked him to be her soul midwife, ensuring her dying days were as she wanted them.
CARERS TO EASE THE LAST DAYS
Soul midwifery is a unique approach to end-of-life care.
In the words of Felicity Warner, the woman who founded it, ‘just as a birth midwife ensures a safe delivery into this world, the soul midwife’s role is to do the same for the dying, to make a good death possible, a dignified, peaceful and even enriching experience’.
This means ‘providing comfort, continuous support and reassurance’ — in practice, after a terminal diagnosis, this involves helping to support the patient as they make an end-of-life plan.
In the final stages the soul midwife might sit by the dying person, holding their hand, playing soothing music and burning appropriate oils. Krista Hughes, a soul midwife based in Chertsey, Surrey, works privately in people’s homes but is often called to a hospice, she says, to work with those with ‘terminal agitation’.
It is a term recognised by clinicians and often managed with sedatives, but as a soul midwife, she prefers gentle breathing, maintaining eye contact and softly repeating the person’s name.
The work of soul midwives was recognised when Felicity Warner was named 2017 End of Life Care Champion by the National Council for Palliative Care and the Royal College of Nursing. The seed for soul midwifery was planted more than 20 years ago when Felicity, now 58, was working as a journalist and interviewed several women dying of breast cancer.
The women told ‘how lonely it felt to be dying despite their medical care and their families around them’.
Not only were their doctors and nurses too busy to talk about death and dying but, surprisingly, Felicity found the women were becoming increasingly distant from friends and family who couldn’t cope with the reality and masked it with platitudes such as: ‘You’ll be feeling better soon.’
Researching how people died before the rise of modern ‘curative’ Western medicine, Felicity found a range of practices ‘that had in common the fact that they respected the act of dying as a sacred time’.
She established soul midwifery in 2004, and has since trained 600 soul midwives — many already have a health practitioner qualification — with an initial three-day course, followed by an apprenticeship lasting around a year.
Qualified soul midwives’ costs are in line with local rates for services such as counselling, though many also work as volunteers at hospices or use the qualification to help care for a terminally ill relative.
Valerie herself had attended a three-day soul midwives’ course shortly after recovering from the cancer surgery in August 2014.
‘It was something she thought she would like to do one day when she was stronger,’ recalls Colin.
So when Valerie told him she thought death might be near, he asked if she wanted him to contact the organisation to arrange for a soul midwife to visit.
Instead, she told him to read her copy of the soul midwives’ handbook so he could take on the role.
For Colin, this meant as well as ensuring Valerie’s comfort, he was her gatekeeper.
While many people want strong intravenous pain control in their last days, Valerie didn’t — ‘she wasn’t in much pain and wanted clarity of thought to the end, yet it took time and effort to stop the palliative care team administering the sedatives,’ says Colin.
‘I had to contact Valerie’s GP and get him to approve her decision, then inform the hospice nurses.’
Three days before she died, the couple celebrated their 17th wedding anniversary. ‘We wrote cards for each other and exchanged presents. The next morning, Valerie told me she had stayed for our anniversary and now she was ready to go. It was her time to die.
‘She had told me she wanted to imagine she was floating away on a boat and asked me to play soothing background music. I lit candles and used essential oils.
‘She had also warned me that the last sense to go would be her hearing, so I read prayers and spiritual affirmations.’
Soul midwifery will not be for everyone. But Colin is in no doubt that it helped Valerie to a comfortable and tranquil death.
‘Of course I longed for a last-minute reprise, a miracle recovery that would keep her with me. But I recognised that Valerie knew what her body was telling her, and did my best to concentrate on our time well spent together. I’m certain she knew that, and appreciated it.’
Complete Article HERE!










