By SONYA VATOMSKY
[A] typical American funeral usually involves a few hallmarks we’ve come to expect: an expensive coffin, lots of flowers, an embalming for the deceased and a number of other add-ons.
But how necessary are those embellishments? Enter the “green burial.”
The specifics of a green burial vary widely, but typically they require far fewer resources for the care of the body and skip a number of the traditional steps, making them better for the environment. Plus, they can save families on funeral costs.
Interest in these pared-down, eco-friendly options has grown as people look for ways to cut their carbon footprint. Nearly 54 percent of Americans are considering a green burial, and 72 percent of cemeteries are reporting an increased demand, according to a survey released earlier this year by the National Funeral Directors Association.
Death planning may not be at the top of your mind, but if you’re curious about looking into a green burial, here’s what to know.
What exactly is a green burial?
The Green Burial Council’s steps for minimizing negative environmental effects include forgoing embalming, skipping concrete vaults, rethinking burial containers and maintaining and protecting natural habitat. Choices can be made at each step of the death care process to limit waste, reduce the carbon footprint and even nourish the local ecosystem.
Embalming, vaults and coffins can be expensive, with the national median cost of a funeral reaching upward of $8,500, according to the N.F.D.A. Replacing them with other options or scrapping them altogether can save money as well as the environment, since you’re not spending on extraneous items or putting them into the ground.
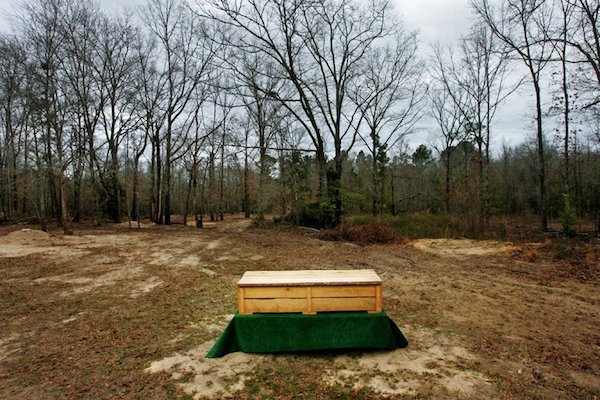
The extent of how “green” a burial can be is up to the individual; the service can be as simple as wrapping the deceased in a cotton shroud before lowering them into the ground. The services can also become more complicated, involving a memorial ceremony and burial in a conservation park like Washington’s Greenacres, where families can choose to plant a variety of plants, flowers and shrubs on the grave.
These aren’t entirely new ideas — the funeral traditions of many religions, for example, are in line with these steps.
Why would I want one?
Death planning is a deeply personal and often unpleasant topic, so reasons for choosing one type of burial over another are as varied as you can imagine. But for many people who opt for a green burial, it can come down to cost, environmental impact and legacy.
Since burial costs vary not just state to state but cemetery to cemetery, hybrid cemeteries — or those offering both conventional and green burials — offer a balanced look at the financial aspect of death. According to the Green Burial Council, a nonprofit that encourages environmentally sustainable death care, most hybrid cemeteries report that graves intended for green burial cost “the same or somewhat less” than their conventional counterparts; after the costs of vaults, coffins and embalming are factored in, the savings a green burial offers are “significant.”
The reason others choose green burial is right in the name: It’s environmentally friendly. Green burials do away with both the embalming chemicals and the extraneous cement, steel or other non-biodegradable materials conventional burials put into the earth, and lack the carbon footprint of cremation, which has been calculated to be the equivalent of a 500-mile car journey.
Perhaps the most personal reason of all is one where the idea of green burial simply speaks to a person. They might find comfort in their body “returning to nature,” or want to take part in a conservation burial, where burial fees are also used to cover land protection, restoration and management. “Not only does conservation burial help protect land, but the burial area becomes hallowed ground, restored to its natural condition and protected forever with a conservation easement,” explains the Prairie Creek Conservation Cemetery. “Citizens who support conservation are offered a more meaningful burial option with the certainty that protected land is the ultimate legacy to leave for future generations.”
But isn’t embalming necessary?
Generally speaking, no. Embalming — the preservation of human remains for public display through the use of a chemical mixture that delays decomposition and makes the body “look natural” — is more of a cosmetic procedure than a public health safeguard.
“The easy elimination in traditional funerals is embalming,” said Amber Carvaly, a service director at California’s Undertaking LA, referring to how to lessen a funeral’s environmental impact.
“It’s almost exhausting at this point to argue with people in the industry on whether it is good or bad,” she said. “You took a body that would have decomposed naturally, you put chemicals in it and a huge part that is left out is that most of the chemicals don’t stay in the body: They are flushed down the drain when they are let back out of the body’s arterial system.”
Still, popular culture tends to reinforce the idea that embalming is a necessary step: Just about 48 percent of people are aware that embalming isn’t needed for a cremation service, according to the N.F.D.A.’s consumer survey.
Jeff Jorgenson, who owns Elemental Cremation and Burial in Washington, said forgoing embalming is a crucial part of green burials.
Instead, he suggested asking for dry ice or Techni-ice, a refrigeration unit, or a nontoxic embalming agent. You can also keep (or bring) the body home and cool it with fans, cooling blankets or open windows.
“Traditional funeral directors will frequently talk about how mom or dad won’t look very good” if the bodies aren’t embalmed, Mr. Jorgenson said. Instead, he has found that families are thankful that his company doesn’t perform embalming “because it feels like there is more room for closure.”
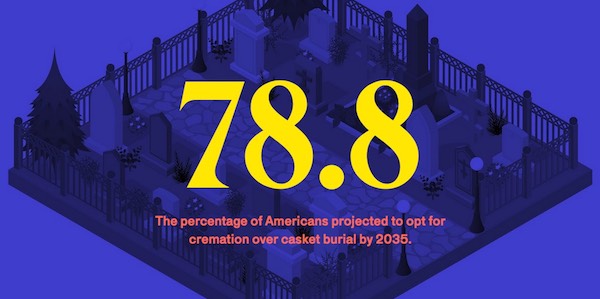
Cremation or burial?
Here is what Americans put in the ground each year through traditional burials: 20 million feet of wood, 4.3 million gallons of embalming fluids, 1.6 million tons of reinforced concrete, 17,000 tons of copper and bronze, and 64,500 tons of steel, according to the Green Burial Council.
Green burials eliminate much of this waste by leaving out almost all of those materials; most bodies are simply wrapped in shrouds made from a biodegradable material like cotton and placed in the ground. And although cremations often have the reputation as being an eco-friendly option, they tend to have an outsize carbon footprint.
(A third option, called alkaline hydrolysis or aquamation, in which water pressure accelerates the decomposition of soft tissues, uses less energy than cremation but is only legal in 14 states.)
Each option has its pros and cons, and it’s important to consider your situation. If you’re attentive to your carbon footprint, cremation in your hometown might still be a better choice than using a green cemetery hours away, and certain funeral homes have ways to offset the environmental hit, like working with organizations on strategic reforestation processes, Mr. Jorgenson said.
Should you go with cremation, there is one final factor to consider: What to do with the remains.
“Even scattering small amounts can be hazardous in a delicate environment such as an alpine environment or vernal pool,” said Michelle Acciavatti of Ending Well, a service that guides families all over the country through their end-of-life options.
Instead of scattering, try Let Your Love Grow, a product that turns ashes into plantable soil for a memorial flower or tree. Another option is Eternal Reefs, which hold cremated remains in an underwater cement ball and create new marine habitats for fish and other sea life.
A ‘green’ burial by any other name
While cremation is a straightforward option, a green burial encapsulates a wider range of decisions, from how to where. If there aren’t green cemeteries where you live, there are still plenty of ways to minimize the burial process’s environmental impact.
Substitute concrete vaults and toxic burial containers for coffins made with sustainably harvested wood and organic liners, and check if products or components were transported over long distances, which can increase the carbon footprint.
You also shouldn’t feel limited by what a funeral home is selling you — by federal law, they’re required to accept a coffin provided by the customer at no extra charge. Or skip the coffin altogether. A shroud made from organic, biodegradable cotton can be purchased through your funeral home or online, or even at the local fabric store.
A growing movement
When it comes to green burials, funeral professionals say the biggest challenge is a lack of awareness and resources.
“Thinking about the impact of disposition on the environment is a new idea,” Ms. Acciavatti said. “And, I would say the other big issue is access: Even though there are over 150 green cemeteries in the U.S. and Canada, there still aren’t enough.”
Ms. Acciavatti and many others in the industry believe that educating the public as well as continuing to invest in green practices helps not just the environment, but humans, too.
“It’s always really rewarding when someone says, ‘I’d really like to return to the earth.’” she said. “And I get to say, ‘I can help you do that.’”
Interested? Start here
The Green Burial Council’s website has information, a list of providers and additional resources for people interested in green burial.
The Order of the Good Death, a collective of funeral professionals, academics and artists, has an informative page about green burials.
Looking for a green burial for you and your pet? Visit the Green Pet-Burial Society.
Complete Article ↪HERE↩!