— What is voluntary assisted dying
Despite the taboo around VAD, the procedure has become legal in the majority of Australian states, allowing those who are suffering to breathe a sigh of relief as they seek to gain some control back in their life, and put dignity back into death.
Whether or not a person decides to access this service, Hall and Wiley said just knowing it’s available has helped to ease the mind of so many Australians.
What is voluntary assisted dying?
Voluntary assisted dying is a medical service offered to those who are eligible, to successfully end the suffering of someone in the late stages of a terminal illness by taking a prescribed substance to end their life on their terms, and as Wiley said, it’s all about choice.
Eligible people can choose if they want to administer the fatal substance themselves, or have a practitioner do it for them; they can choose when and where they’d like the event to take place, ensuring providing comfort and dignity in death.
VAD was kickstarted in Australia by broadcaster Andrew Denton, who watched his father suffer a “drawn out, desperate death”. Denton’s charity, Go Gentle, has played a major role in getting VAD laws passed in all Australian states.
So, what are the eligibility requirements?
A person must be:
- diagnosed with an advanced disease or medical condition that will cause death within the next 12 months;
- is suffering from intolerable levels of pain and discomfort;
- is of sound mind to make the decision;
- is acting voluntarily and without coercion;
- is at least 18 years old;
- an Australian citizen or permanent resident.
The process
Given the gravity of making the decision to undergo voluntary assisted dying, it’s not as simple as just asking for medication.
A person must make three request’s to a medical practitioner within the designated 9-day period. However, once a request is made, and right up until the administration of the fatal substance, there is no obligation for the person to follow through with VAD.
Once the first request has been made, a person will need to undergo a consulting assessment to ensure eligibility, and once the final request has been made, they will then need one final review before the official administration decision is made.
The assessments must be completed by two separate doctors who have received mandatory VAD training.
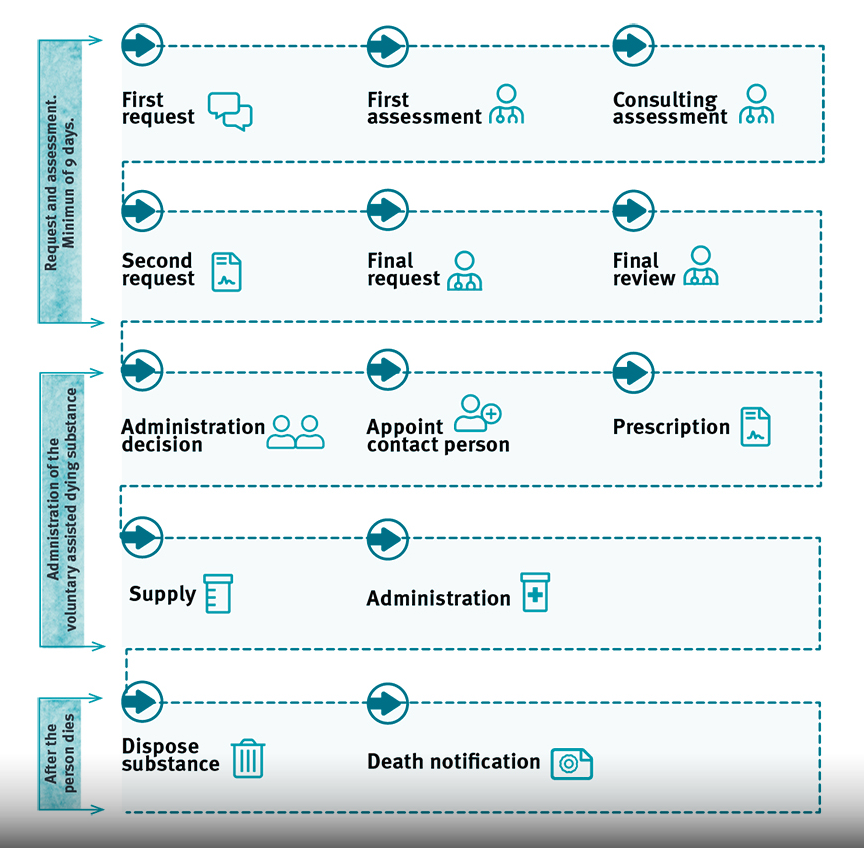
Whilst practitioners can refuse to participate based on conscientious objection, the doctor must still inform the patient of the process and provide other practitioners names who can assist; the same goes for religious facilities, they cannot stop or inhibit a practitioner from fulfilling their job at the request of a patient.
Once the process is completed, a touching detail to ensure dignity is maintained even after death, VAD will not be written as cause of death on a person’s death certificate; it will simply state the illness or medical condition the person was suffering from.
By allowing a dying person to take control of their death, dignity can be restored to its fullest.
Complete Article ↪HERE↩!
