Two very different books about death, by Kathryn Mannix and Caitlin Doughty, look at how we can face our final days with practicality, adventure and joy
[W]hen John Keats was dying of TB in Rome, just 25 and far from family and home, he wrote a series of beautifully judged, empathetic letters of farewell that deal lightly (yet never falsely) with his physical suffering and his emotional anguish. From the shrinking circle of his life, from his frail body drowning in itself, he reached outwards towards the friends he was leaving. In his final letter, he wrote of living a “posthumous existence”; his last phrase becomes his eloquent, courteous and self-effacing goodbye before he exits the stage on which he has had such a small parcel of time: “I always made an awkward bow.” Dying as a performance, dying as an art and a practice, dying as something solemnly profound and sorrowful and at the same time as normal, natural; dying as physical and as spiritual; dying as the end of a whole world because, as Oliver Sacks wrote, when dying himself: “There is no one like anyone else, ever.”
We live in our bodies and die in our bodies. In previous centuries, death was familiar and not hidden behind institutional walls: before the 20th century, there would have been scarcely an adult who had not seen their parents, some of their children, and their friends die. Moreover, there was faith that it was not the end. People witnessed death, dealt with it, prepared for it, even embraced it (John Donne used to sleep in his own coffin; Jeremy Taylor wrote his 17th-century manuals for the soul, Holy Living and Holy Dying, which became the preeminent works of the ars moriendi tradition; in The Tempest, Prospero consigns himself to an old age in which every third thought will be of death). Now, although we live with the sense of our own ending, we don’t really. We know we’re going to die, but we don’t know. Our body doesn’t know, except in dizzying moments of terror, until the sentence has been uttered and the gallows are being built under the window. Even then, death is often held at bay and life prolonged at all costs: the fragile and disintegrating body is plugged into machines, pumped full of oxygen and blood and drugs, its gallant heart restarted and kept going, no matter the pain, no matter the hopelessness of the endeavour, no matter that at a certain point this isn’t living, just a slowed-down, drawn-out, painful and undignified dying.
It has become easier to live longer, but harder to die well. Most people want to die at home; most die in hospital. Most want to be with family; often they are alone or with strangers. “Their death has been stolen from them,” writes Seamus O’Mahony in his bracing and unsentimental account of dying, The Way We Die Now, which charts how something that used to be public and acknowledged, with a common script, has become an aggressively medicalised and bureaucratic process placed in the hands of experts; sometimes banal, sometimes farcical, sometimes painful or undignified. Modern, sanitised death becomes a dirty little secret, almost embarrassing: our language circles round it, we don’t like to name it, cross the road to avoid those recently touched by it, and shy away from the physical, squeamish fact of it, so that the dead body is whisked away, frequently embalmed (for fear of its smell), cremated in “facilities” that are often in industrial zones.
Have we lost our way with dying and with death? In the last few years, there has been a crowd of books by doctors, scientists, writers and people who are scrutinising their own departure that have sought to show us different, kinder ways of ending: Atul Gawande, Oliver Sacks, Henry Marsh, Jenny Diski, Tom Lubbock, Marion Coutts, Paul Kalanithi, the luminous final poems of Helen Dunmore… the list is long. Behind them all stands the austere, magisterial work by Sherwin Nuland written in 1993, How We Die. Now Kathryn Mannix joins this distinguished group and her voice, though quiet and calm, is distinctive. A palliative doctor (or “deathwife”), she spends her days with the terminally ill and their families, witnessing and supporting them at times of intense suffering, terror and loss. About a quarter of deaths are sudden and unexpected, but she usually sees the ones that come slowly, over months or years, and while much of her work is diagnostic and medical, one of her crucial tasks is to help those who are dying and their families find ways of dealing with life’s final, great event.
With the End in Mind: Dying, Death and Wisdom in an Age of Denial is Mannix’s account of ways of dying, through a series of vivid stories, most of which disguise the protagonist, some of which are composite tales stitched together from several cases, and all of which are heart-wrenching testimonies to human courage and love. Her purpose is to describe many forms of death – the young man with testicular cancer treated in the room dubbed “the Lonely Ballroom”, the dying mother in the hospice who manages to walk her daughter up the aisle, the 22-year-old with cystic fibrosis, the teenager with leukaemia – and to show how in each case, while a death may be emotionally harrowing, it need not be intolerably painful; while it may be tragic, it need not be ghastly or full of the chaos that accompanies too many ends.
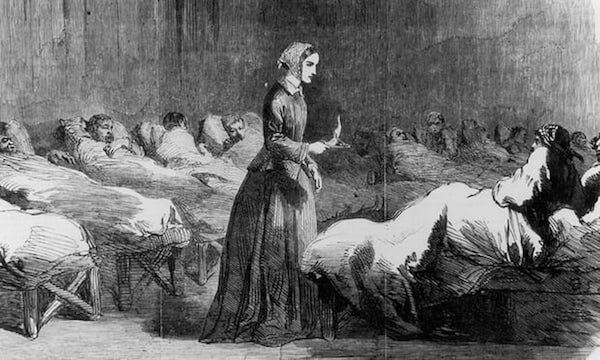
Like those romantic portraits of Florence Nightingale holding her lamp aloft as she walked between beds of maimed and dying soldiers, Mannix’s aim is to shed a soft, clear light on a subject she feels is too often avoided. She wants us to think about what dying and death mean for others and for ourselves and take the fear and recoil out of the subject. Mild, tender and conciliatory, she is punctiliously even-handed. If one story shows how denial is toxic and the truth needs to be gradually and gently revealed, in another she demonstrates the usefulness of denial; if one describes how precious time can be won for a patient, another is an example of how prolonging life can be cruel and death a necessary kindness. One person’s good death is not another’s – we all need to find our own way to take our bow and leave the stage.
I agree with almost everything Mannix says; I would like her, or someone like her, to be my compassionate, wise doctor when I lie dying, easing me out when my time has come. Yet in her desire to show that death can be well managed, she leaves out the mess, fear, pain and unpredictability of so much dying – its scandal, its wildness and its impossibility. Not all passing can be gentle and not everyone can be brought to acceptance in the face of their own obliteration. However we dress it up and think about it, death remains blankly ungraspable and stark.
Enter Caitlin Doughty, American mortician, joyful member of the death-positive movement, who describes what happens to our mortal remains with boisterous relish – “ya tell it like it is”, she wrote in her first book, Smoke Gets in Your Eyes. Skin slip is skin slip; putrefaction stinks. The body fails and the body rots and death is a tragedy and a farce. Jaunty, boisterous and unsentimental, Doughty believes that we in the west have made death and its aftermath into a corporate, perfunctory affair, in which the meaning of an ending is denied. Her mission is to “reclaim public understanding of dying” and to bring individuality and joy back into our dealings with the dead – and so, in From Here to Eternity, she embarks on a journey of discovery: to the only open pyre in America; to a sky burial in Tibet, where the body breaker slices the corpse into parts, pounds the flesh with a mallet, mixes it with barley flour and yak butter or milk, and leaves it to the shrieking vultures to consume; to burial towers in India; to the people of Tana Toraja in Indonesia, where mummified bodies are cared for in their home (offered food, dressed, even given a bed with the living) over months or years until the family can sacrifice an animal and put the dead to their final rest; to Barcelona’s mass bone pits; Mexico’s Day of the Dead. Skulls used as flowerpots, bodies made into compost on a body farm, corpses covered with rose petals, funerals conducted by men with dreadlocks and purple frock coats – what Doughty relishes are those rituals that acknowledge death, its bodily fact and its emotional enormity.
And although the book is in love with extremes, it actually shares Mannix’s desire to be balanced: one culture’s practice is another culture’s taboo. We might not like the thought of ripping the rotting flesh from our loved one’s bones, but for some, burning a body is equally repugnant. What is important is “to hold the space” – to banish our fear and shame, and create a ring of safety around the grieving family and friends where they can mourn, each in their own way.
Animals perish; only humans die – because we are creatures who are aware of our own mortality. This awareness, which can feel vertiginous, unendurable, is also what gives us selfhood, and life shape and meaning. “Death destroys a man; the idea of death saves him,” wrote EM Forster. It is Henry James’s “distinguished thing”, Martin Amis’s backing to the mirror, Rochefoucauld’s sun that we must not stare at too long lest we go blind with seeing. It’s the great nothing; the everything, which makes us and unmakes us, and to which we all come in the end. Nothing is more certain; nothing more bewildering, strange, scandalous, downright impossible, forever true.
Complete Article ↪HERE↩!

