She arranges everything, from finding long lost families to organising organ donation
She’s only 26 but Claire Wretham is employed by a Welsh hospice to help people face death.
She is the youngest person in any of Marie Curie’s nine hospices nationwide in the role.
Watching her own grandmother have “a beautiful death” inspired her to help others do the same.
“We all deserve a good death that celebrates life. I am helping people feel at peace,” she said.
As full time spiritual care co-ordinator at Marie Curie Hospice, Cardiff and the Vale , Claire answers any questions patients and their families have about life’s greatest mystery.

“My grandmother died at home, a really beautiful death with all her family around her. We were able to facilitate for her the perfect death.
In an increasingly secular and diverse society her role at Marie Curie has replaced the traditional one of chaplain, although Claire still uses that term when first meeting patients.
“I introduce myself as chaplain because it really is a modern interpretation of that,” she explained.
“My age is mostly irrelevant. People often comment on the fact I am young but I don’t think it hinders my role.
“People my age group see the world differently and approach things in a different way.
“Part of my role is asking people “what makes you you, how would you describe yourself and how do you find peace?
“As younger people we often have lots of spaces and experiences to express ourselves, but some older people don’t feel the same freedom to express themselves, so I ask “who are you, what makes you you and what makes you comfortable and at peace?.”
A practising Christian, Claire was appointed to the job two years ago and is an “allied health professional”, not a medic, although she knows and can explain what may happen during dying and immediately after.
Her role as spiritual adviser was created in response to research that Marie Curie did in 2015 investigating how to improve access to palliative care for people with dementia, learning disabilities and people with different or no religious beliefs.
Sarah Lloyd-Davies, hospice manager at Marie Curie Hospice, Cardiff and the Vale, explained: Hospice care and chaplaincy services have long been rooted in the Christian tradition, as both developed at a time when Christianity was the majority religion in the UK.
“As the country has grown more diverse there has also been a trend in growing numbers of people identifying as nonreligious.
“The hiring of a spiritual care coordinator to replace the traditional chaplain role at the Marie Curie Hospice Cardiff and Vale reflects the feedback from our local community, which recognises that one person and one approach cannot meet everyone’s spiritual needs.
“In order to make sure our services are truly inclusive and person-centred, we need to focus on connecting with belief-based communities and exploring new ways of providing spiritual care so we can ensure people feel supported in the best way for them at the end of their life.
Whatever background people come from death and dying are still taboo subjects which Claire must help them face.
“A lot of my job is myth busting and explaining to people how it works at the hospice and what they can expect as they come to the end of their life,” the 26 year-old said.
“Questions I would normally ask are whether they have any spiritual or religious needs and whether they have a faith or anything that’s a source of comfort.
“If they are religious I will discuss that with them – for instance if they are Catholic and want the last rites I liaise with their priest, if they are Muslim and want their bed facing Mecca and halal meals my job is to arrange that and liaise with nursing staff about it.”
There is “no formula or prescription” for talking about death so Claire begins with a few questions.
“It’s about asking questions to get people to explore death or go away and think about it.
“The sort of questions I’ll ask are things like – have you got any unfinished business or anything you want to tie up? That can be relationships, writing a will, funeral planning, making amends with estranged family members , and how we can help with that, if we can.”
When patients tell her they are scared of dying she tries to remove some of the mystery around it to reassure.
“If someone is scared of dying a big part of it, from my point of view, is explaining what will happen when they die.
“There are lots of misconceptions about pain relief. They want to know what it will feel like. I explain that they will probably just fall asleep more.
“I explore with them what they think that will be like. There is nothing you can say really, ultimately it’s something people form their own ideas about.
“I may also ask people what they want their legacy to be. Some people think there is nothing after you are dead so I’d ask them how they want to be remembered.”
But she doesn’t push it if people don’t want to talk.
“We live in a culture where it’s normal to talk about things but the idea of a chaplaincy and spiritual support is so alien to some people that they say no, they don’t want to talk to me.”
As she doesn’t have all the answers Claire tries to keep things practical when explaining what happens after death in a hospice.
“I know what a dead body looks like, where you go after death and what the crematorium looks like.
“My main technique is to remove any confusion. I do ask people if they are frightened and how I can help them not feel afraid.
“Most of the time people are worried about “what’s happening next and what about the pain?”
“I think death is so difficult to talk about because we don’t see death often. The majority of deaths happen in hospital. People don’t know what death looks like.
“For us in a hospice a huge part of our role is pulling the curtain on that. Lots of people come in asking really big questions and having misconceptions.”
These include controversy and suspicion surrounding syringe drives to administer pain relief and the mistaken beliefs about how they are used.
“People are horrified by the syringe driver. It’s in a locked box and nurses replenish pain killers. It is controlled pain relief. Some people think it is a death sentence, but it’s not. Sometimes people have a syringe driver for pain relief and then have it removed.”
“On the other hand some people say “can I have the drugs now?”. That’s not legal and not what hospices are about.”
“When we talk to people here about donation it’s usually only corneas because they can’t donate anything else. Some people say “you can take anything but not my eyes, but I have watched eyeball removal and it is really amazing because one cornea can be used to help eight people.”
It is Claire’s job to arrange any donations. She recalled one case when she arranged for a motorbike to collect the brain of a patient with motor neurone disease who had requested it be donated to medical science – something that had to be arranged within 72 hours.
“I spent all day organising brain removal and that afternoon someone came down from London on a motorbike and took it back for donation to medical science.”
Although her job does involve these practical matters it is also a matter of listening to people at what can be the hardest time of their lives.
“My job is varied Once a man came in and said his father had died here 28 years ago. He said he had never visited Wales and now lives in Canada but had flown into Cardiff to see where his father died.
“I showed him around the hospice and talked to him about his grief and about Penarth. He was very tearful, he had flown all the way from Canada to see where his dad died, but he was able to resolve his grief.”
Surrounded by grief and death on a daily basis Claire says it is not morbid but a privilege to help people.
“Death happens to everyone. It’s coming to all of us. We should look to normalise it.”
Complete Article ↪HERE↩!
The case for hospice care
By BETH SLEPIAN
A recent analysis published by the New England Journal of Medicine revealed that for the first time since the early 20th century, more Americans are dying at home than in the hospital.
According to the report, in 2017, 30.7% of Americans died at home, while slightly fewer (29.8%) died in hospitals. Another notable statistic from the study is that between 2003 and 2017 the number of Americans who died in hospice-specific facilities grew by 41%, from 0.2% of deaths in 2003 to 8.3% in 2017. According to the National Hospice and Palliative Care Organization (NHPCO), 47.5% of New Hampshire residents on Medicare who died in 2017 were receiving hospice care benefits.
This data does not come as a surprise to those of us who work in hospice care and have the honor of helping families navigate the end-of-life experience.
Up until the mid-1900s, it was routine for people to die in their homes, cared for and surrounded by loved ones, but by the 1950s, more Americans died in hospitals. The concept of “death with dignity” was introduced in the United States in the early 1960s, sparking the movement toward hospice care.
The hospice movement gathered steam in the late 1970s with the formation of the National Hospice Organization, and by the mid-1980s, the federal government formalized the hospice benefit for people on Medicare.
Concord Regional VNA has been caring for people in their homes for 120 years, providing nursing, therapy, personal care, homemaking and other services to people of all ages. For more than 30 of those years, we have provided specialized end-of-life care, guidance, and support to patients and families. In 1994 we expanded our hospice service by opening the first Hospice House in New Hampshire on Pleasant Street in Concord. We have served thousands of hospice patients and their families over the years, including nearly 1,000 patients in 2019.
While it is true that hospice care comes into play toward the end of a person’s life, there are many common misconceptions, such as:
■ Hospice care is only for the last few days or weeks of a person’s life;
■ It is only for people with cancer, people in severe pain or those who have a “do not resuscitate” order;
■ People on hospice do not receive treatment, they’re just kept comfortable with medication;
■ Hospice is a “place” where a person goes to die;
■ Hospice hastens death;
■ People on hospice must give up seeing their primary care providers;
■ Hospice care is focused on the patient and ends when the patient dies.
Hospice care is much more than meeting patients’ medical needs. Hospice care empowers patients to have a voice in their end-of-life experience, and to help them through it with as much comfort, grace and dignity as possible. It is about compassion – for them and their loved ones.
Some people choose to begin receiving hospice care in the final weeks or days of a terminal illness, but it is not unusual for patients to begin hospice care many months before they eventually pass.
People who receive hospice care through Concord Regional VNA benefit from individualized care coordinated with their care team, which may include their primary care provider and other clinicians. They may receive nursing care, physical and/or occupational therapy, pain management, spiritual care, social work , including emotional support and companionship – all in the place they call home, which could be a private residence, an independent living or assisted-living community, or a skilled nursing facility. Those who need more intensive care may opt to receive care at Hospice House.
Equally as important in this journey are the caregivers, who are most often the patients’ loved ones. Hospice care is about them, too. In addition to day-to-day assistance with patient care, loved ones may receive emotional and spiritual guidance and support from our counselors and spiritual care providers; help with end-of-life planning; much-needed respite care; and myriad other services. And it is important to note that hospice care does not end when a patient dies – our bereavement counselors and support groups help loved ones as they learn to cope with their loss for as long as they need us.
Hospice care is also about volunteers. The hospice movement was started by volunteers and they remain a crucial component to this day. In fact, Medicare requires that volunteers provide at least 5% of total patient care hours, which can take the form of direct support, spending time with patients and families, or performing tasks that support hospice care services. Concord Regional VNA is incredibly fortunate to have nearly 100 volunteers from the communities we serve who give their time and energy to our hospice patients and their loved ones.
So what does this mean and why does it matter? The recently released data suggests that more people have come to understand that receiving care in the comfort of home – in familiar surroundings, in proximity to loved ones and friends – is a preferable and realistic option. From a clinical standpoint, studies show that patients who receive hospice care live longer than those with similar diagnoses who do not receive hospice care. Receiving care at home also has a significant positive impact on overall health care costs.
Death is a fact of life. Patients often tell us that choosing hospice allows them to feel in control, and managing their symptoms helps them feel more at peace. Choosing hospice is not giving up, rather, it is choosing to live fully until you die.
It is not meant to be scary; it is meant to help people live each moment to the fullest and to pass with dignity and respect surrounded by love.
We at Concord Regional VNA are privileged to help patients and their loved ones navigate this journey, and proud to have been providing hospice service to the people of Concord and the 43 other New Hampshire communities we serve for more than 30 years.
Complete Article ↪HERE↩!
‘It was kindness and it was a mercy’:
The doctor helping people to die
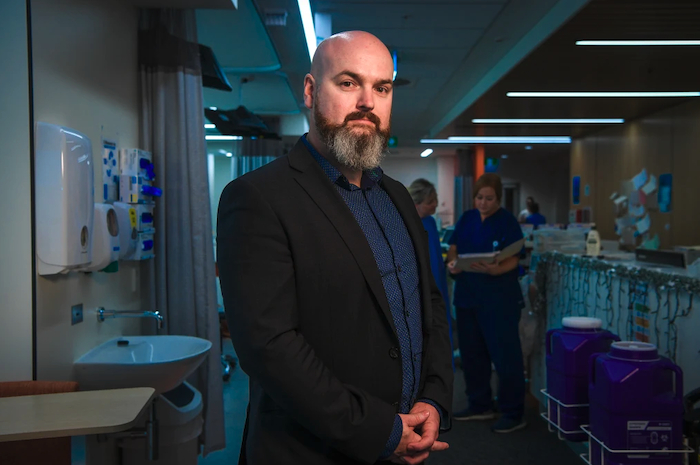

It was just after 2pm on October 31 when oncologist Cameron McLaren arrived at Phil Ferrarotto’s house on the outskirts of Melbourne to help him die.
Dr McLaren had never administered a fatal drug to a terminally ill patient before. He was struck by the magnitude of what he was about to do.
“I had no idea if I was going to be OK with it even up to the point where I put the needle to his arm,” Dr McLaren said. “But there was no question that this was the right thing to do for Phil. It was what he wanted. It was kindness and it was a mercy.”
Phil hadn’t eaten for days. No longer able to digest his medication, the 70-year-old was hooked up to an intravenous morphine drip and sustained by spoonfuls of cola-flavoured ice.
He lay in bed with his daughter Katie and wife Dorrie curled up on either side of him. They cuddled his frail body and watched his chest rise and fall with each painful breath.
His son Glen and son-in-law Ryan came into the room with three glasses of aged Glenfiddich whisky; one for each of them and one for Phil.
They toasted Phil as Dr McLaren gently swabbed the father-of-two’s arm with medicinal alcohol.

Dr McLaren found a vein and inserted a cannula. He used the thin tube to inject a sedative medication, before administering an anaesthetic and a muscle relaxant.
Phil began to drift off within minutes of the drugs flowing into his bloodstream. The circle of his family closed in around him. They held his hands and told him how much he was loved. “Be happy,” Phil said, before he took two final, deep breaths.
Dr McLaren has helped two dozen terminally ill Victorians apply for permits to end their lives since the state’s voluntary assisted dying laws came into effect on June 19. Eleven of them have since died using the legislation.
All the patients Dr McLaren has assessed so far were in intolerable pain and often bedridden.
“The number one reason people are doing this tends to be more the existential suffering,” Dr McLaren says. “It is the loss of joy, the fear of losing dignity and the fear of losing autonomy and of being a burden to family.”
Cancer-stricken patients surrender their bodies to years of treatment they know will cause them pain and discomfort, Dr McLaren said. He wants to give people control at the end of their life.
“It is one last decision about their body which is entirely theirs,” he said. “This is something we do for animals and when they get too old and they are suffering greatly. We put them out of their misery and we call it humane. Why shouldn’t we afford humans the same humanity?”
When Dr McLaren first met Phil he was sitting in an armchair in his living room hooked up to an oxygen concentrator. The cancer had spread from his bladder to his lungs and had riddled his bones. Then it invaded his liver, causing his belly to swell and fill with fluid. Opioids prescribed to Phil did little to dull his pain. Each breath was agony.
This kind, strong-willed, clever, retired general manager, who had battled four different kinds of cancers over the past 18 years, was frank and direct.
He told Dr McLaren he wanted to end his own life.
Dr McLaren carefully assessed Phil. He ticked off all the strict criteria; over the age of 18, of sound mind, an Australian citizen with less than six months to live. He referred Phil on to a second doctor who also deemed Phil eligible for the scheme.
Before his application was approved an email from Phil arrived in Dr McLaren’s inbox: “This gives me no pleasure in begging you to end my life, but I have no one else to turn to. I’m struggling with every breath I take and I can’t do it anymore.”
A permit for a doctor-administered death was approved the same day by the Voluntary Assisted Dying Board with Dr McLaren agreeing to administer the fatal dose.
For days after Phil died, Dr McLaren was waiting for the “hammer’s fall”.
“I was really concerned about the fallout for me, personally and emotionally,” he said. “I was concerned about being recognised as ‘that’ doctor and the impact it might have on my family and my work.
“I didn’t question what I did, because in Phil’s case, he was in the last days of his life and he was going to die within 48 to 72 hours. I was able to provide him a death that in his mind was dignified. It didn’t cost him anything. It cost him his suffering.”
The fallout never came.
“It was a lonely experience because there’s no literature review you can read on it,” he said. “It still does feel lonely because there’s not a lot of us doing it.”
The night Phil died, Dr McLaren picked up his two year-old daughter when he got home and held her in his arms. His love for his child overwhelmed him and he pressed his face against hers.
“As I was holding her I thought of Phil being surrounded by his family as he took his final breath,” he said.
“Nothing that we could have done would have avoided his death, but we were able to make sure Phil died at home in the arms of the people who loved him most. I thought, yeah, that would be a nice way to go.”
Before he died, Phil wrote a letter to Dr McLaren thanking him for what he was doing:
Complete Article ↪HERE↩!
To Die Is Different From What Anyone Supposed
Art, philosophy and mortality.
At an overlooked moment in his Essays, Michel de Montaigne writes that “life itself is neither a good nor an evil; life is where good or evil find a place, depending on how you make it for them.” Yet it’s hard for anyone to reckon, before the point is moot, how much good and evil one life shelters in its span. No matter what we do while we’re alive, there’s plenty that we leave unfinished, or that we gape at while it goes awry. There are mistakes that we still might have enough time to mend. Hamlet got it backwards: it’s not death, but life, that “puzzles the will” with its ironies and uncertainty.
Every now and then, however, people manage to outlive themselves. Convicts serving life sentences do, for example, which is why “Folsom Prison Blues” is such a savage, luminous song. Mortally ill people sometimes end up in an equally uncanny position. Leo Tolstoy’s character Ivan Ilych, on his deathbed, glimpses the ugly truth of his life: “It occurred to him that what had formerly appeared completely impossible to him, that he had not lived his life as he should have, might be true. It occurred to him that those barely noticeable impulses he had felt to fight against what highly placed people considered good, barely noticeable impulses which he had immediately driven away—that they might have been the real thing, and all the rest might have been not right.”
Russian literature is full of people like Ivan. Prince Myshkin (in Fyodor Dostoevsky’s novel The Idiot) eventually realizes that “for a long time now, he had not been talking about what he needed to talk about, and had not been doing what he needed to do.” The horror of this realization breaks his spirit, and he succumbs to seizures and catalepsy, dead to the world. A quieter storm breaks over Lambert Strether’s head in The Ambassadors, by Henry James: “I’m too old…What one loses one loses; make no mistake about that. Still, we have the illusion of freedom; therefore don’t, like me to-day, be without the memory of that illusion.”
Outcries of regret like these carry an emotional charge for us, the audience, that can be hard to explain. Is the finality of death, prison, or old age really profound just because—to quote Michel Houellebecq—the goal of life’s been missed? Critics have spent their whole lives on the works of Henry James only to conclude that “the idea of ‘too late’” was some kind of regrettable obsession on James’s part (see, e.g., Berthold 1983). After all, the curtain does have to fall, sooner or later.
Fortunately, these epiphanies that reach us from death’s farther shore aren’t really bemoaning lost opportunities. Instead, they are bits of fire carried down from those Olympian peaks where life appears as it really is: a frenzied circus of petty motives, bootless efforts, and misunderstandings. Death is the greatest moral agent in all of life. It boils each individual down to her most generous acts; nothing else survives. We are the sum of our gifts to the people who will outlive us. Thus it does matter what a dying man decides to regret. His regrets, useless to him, are the bitter correctives that we survivors may choose to adopt.
Literature’s stuffy cousin, philosophy, is always playing a game of death. The philosopher tries to abstract truths about life from human experiences, impartially, as if she hadn’t lived them herself. Baruch Spinoza famously wrote that philosophy should consider the world sub specie aeternatis, “from the perspective of eternity.” Erasmus, in The Praise of Folly, paints a vivid picture of Menippus (who, supposedly, lived on the moon) doing just that:
“If a man like Menippus could look down from the moon and behold those innumerable rufflings of mankind, he would think he saw a swarm of flies and gnats quarreling among themselves, fighting, laying traps for one another, snatching, playing, wantoning, growing up, falling, and dying. Nor is it to be believed what stir, what broils, this little creature raises, and yet in how short a time it comes to nothing itself; while sometimes war, other times pestilence, sweeps off many thousands of them together.”
It’s a comical picture, but there’s a great deal of forgiveness in it as well. When it’s our turn to die, there’s no longer any reason to stay angry at people who loved us, or cheated us, or whom we envied. Recrimination and bitterness lose their impetus. The facts of life don’t alter just because we die; if we lived forever, we’d still behave like idiots from time to time. But the fact of death, seen clearly and steadily, drags many other things with it into the light. At the moment of his death, when he’s murdered, Lester Burnham (in American Beauty) “can’t feel anything but gratitude for every moment of my stupid little life.”
Philosophy as we know it began when Plato sat down and tried to make sense of the murder of Socrates; the vicious Athenians who killed him to preserve their monopoly on morals become, in The Republic, simple cave-dwellers frightened of sunlight. Their cruelty is pardonable blindness; in order to write about the death of Socrates, in a fashion that honored his greatness, Plato had to make peace with his teacher’s executioners.
We tend to think of “objectivity” as a cold, rational perspective that doesn’t take sides on questions of morality. We associate it with empirical observation and scientific testing. That’s a tremendous misunderstanding. To be objective is to grasp something as a whole. It lays bare the threads that connect a senseless murder in Reno with a “fancy dining car” on a passing Folsom train. It’s realizing, as Plato did, that Socrates couldn’t have become so widely known and admired in a city less dangerous to him than Athens. It means remembering, like Ivan Ilych, the impulses towards something better that one felt, repressed, ignored, all for the sake of a life not worth living in the first place.
Walt Whitman wrote, in his “Song of Myself,” “to die is different from what anyone supposed, and luckier.” For, as he says in the preceding line, “All goes onward and outward, nothing collapses.” To see that, instead of just divining and proclaiming it, is the work of philosophers: those few who teach themselves to die with eyes open.
Complete Article ↪HERE↩!
Vancouver photographer offers solace to those dealing with death
Grief Narratives website allows users to reflect on the end of days
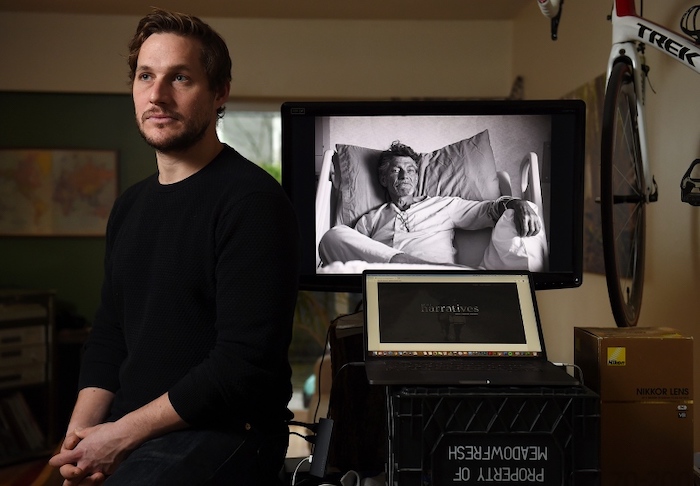

By John Kurucz
Josh Neufeld has a special affinity for turkey necks.
It’s not that they taste particularly good, nor were they a staple on his plate since childhood.
Neufeld’s late father Dietmar loved the neck. It was his go-to whenever turkey was served at a holiday meal.
Dietmar died in September 2015 after a brief battle with cancer.
Thanksgiving dinner that year was the first family gathering after Dietmar’s death.
“I sat in his spot and in his honour, I ate the whole neck and blubbered like a buffoon because it was like ‘OK, this is our life now,’” Josh recalled. “It’s four Christmases later, but still that feeling doesn’t change. It sucks.”
Outside of the culinary nod, Neufeld continues to pay tribute to his father in a manner that’s profoundly personal, yet completely universal.
Neufeld’s website Grief Narratives invites people the world over to share their photos, thoughts, feelings and emotions as they experience death in their own unique way.
The online platform has garnered interest across Europe and as far away as South Africa.
The site was born partly out of Neufeld’s experience photographing the end of his dad’s life, a project called Meeting Mortality.
Across roughly 30 photos, Neufeld documented the final 19 days of his father’s life in hospital.
“My dad never did see the photos, which really messes with my head,” said Neufeld, a professional photographer by trade.
Neufeld hatched the idea in the spring of 2015 upon visiting a dying relative in California. His uncle was simultaneously battling Parkinson’s disease and cancer and sat the roughly 50 family members down to prepare them for the end.
“You walk away from a conversation like that and you’re like, OK, that really realigns priorities and shifts perspective and helps you look at life a little differently,” Neufeld said.
Volunteering at a hospice was to be Neufeld’s next step but Dietmar fell ill before his son could find a volunteer placement.
Dietmar was diagnosed with pancreatic cancer on July 13 and died Sept. 9. He was 66. He was the department head of classical, near eastern and religious studies at UBC, an avid cyclist and loved taking the piss.
“Him and I would spend hours out by the fire chatting,” Neufeld recalled. “He could go deep about anything religious and he taught ancient Greek language. But then he could also sit there and shoot the shit about the most meaningless, stupid stuff.”
Documenting the end was done so with his Dietmar’s blessing. He also came up with the name “Meeting Mortality.” Neufeld discussed the idea with his mom and three sisters and got buy-in, though not totally.
“My oldest sister doesn’t really like to look at those photos,” Neufeld said. “But I think they just understood where it was coming from.”
Neufeld has since gone on to photograph the end of days for other families. Last year, he interviewed 22 people about their experiences confronting mortality, taking photos as they spoke.
He hopes to expand Grief Narratives into a multi-media platform where users can pay tribute to loved ones via text, photos, video and other media.
It’s a project not necessarily intended to normalize death, but to give community and a space to reflect for those who need it.
“I hope it becomes something people use and find value in,” he said. “I’m trying to show people that it’s an option. It’s not going to be for everyone.”
Neufeld’s work can be seen online at griefnarratives.com and joshneufeldphotography.com.
Complete Article ↪HERE↩!
The struggle to create a new craft of dying
—what is medicine’s role?
By Richard Smith
“Lyn Lofland’s The Craft of Dying (1978) is one of the most important books on post WWII death and dying practices that almost no one has read,” writes John Troyer, director of the Centre for Death and Society at Bath University. He thinks that everybody interested in death and dying should read the book. I agree. Potentially that means that every human being should read the book—because who cannot be interested in death, arguably the most important thing about us. Plus The Craft of Dying is short, easily read, full of compelling stories, and constructs a clear argument.
“Death can neither be “believed” nor “magicked” nor “scienced” away,” writes Lofland in her first line. But we can’t stop ourselves from thinking about it: “Everywhere and always humans think about it and develop beliefs regarding it and produce emotions toward it and do things relative to it. What they think, believe, feel, and do is, of course, variant. But that they think, believe, feel, and do is a universal.”
Every culture has developed beliefs and customs around death, but human death, argues Lofland, has changed dramatically in the past 60 years. Until that time people died mostly of infectious disease and injuries. The period of dying was short, and it was clear when people were dead. Medicine had little to offer. Now people die mostly of chronic disease, and the length of dying is long. Death is not easily defined, and doctors have much to offer, including long term ventilation, heroic operations, and drugs, some of them extremely expensive.
“In the past few decades, medical science has rendered obsolete centuries of experience, tradition, and language about our mortality, and created a new difficulty for mankind: how to die,” writes Atul Gawande in Being Mortal, published in 2014. Lofland wrote something similar in 1978: “There exists currently no widely accepted, fully articulated, well-integrated dogma that gives ‘being dying’ its meaning or its place in the larger scheme of things.”
A cultural vacuum has been created, and inevitably attempts are underway to fill the vacuum. We have entered a new age of what Lofland calls “thanatalogical chic”: in the contemporary cliché “death is the new black.” We have to decide how to die, where to die, how to dispose of the dead, how to mourn, and, most difficult of all, what death means.
One response has been what Lofland teasingly calls “the Happy Death Movement.” It is an inchoate social movement with many practitioners, strands, and different views, but Lofland sees patterns that were emerging in the 70s and are still emerging.
Firstly, a social movement needs an enemy, and the enemy of the Happy Death Movement is death denial, death as the great taboo. Lofland defines the enemy: ”America is a death-denying society…death is a taboo topic…death makes Americans uncomfortable so they run from …death is hidden in America because Americans deny it….” For America, Lofland’s home, we could substitute any high-income country—or even any high-income group within a poor country. “The consequences of all this denial and repression are,” continues Lofland, “asserted to be quite terrible: exorbitant funeral costs and barbaric funeral practices, inhumane handling of dying in hospitals, ostracism of the dying from the living, inauthentic communication with the fatally ill, an unrealistic, mechanical, non-organic view of life, and so forth.”
Lofland is dismissive of the idea of death as taboo: “One might consider it somewhat odd that the statement that death is a taboo topic in America should continue to be asserted in the face of nearly a decade of non-stop talking on the subject.” Talk, writing, and storytelling about death has continued unabated ever since and probably increased. It is probably fair to say, however, that there is much less familiarity with the experience of death: dying people, the signs of death being close, dead bodies, and the disposal of the dead.
A social movement also needs something to shoot for, and for the Happy Death Movement it’s some form of idealised premodern death, with the dying person at home surrounded by loved ones and calmly bidding them goodbye. Lofland is dismissive of this as well, including in her book stories of the dying being buried alive (in Samoa) and ignored while families party (in Tahiti).
As you would expect, the attempts to create new behaviours and beliefs around death reflect broader cultural trends, which Lofland identifies in the United States as “ ‘humanistic-counterculture’ denouncement of modern society in general, which denouncement emphasizes the Western world’s dehumanizing, unemotional, technologically dominated, inauthentic, and constricted character.” That cultural trend is alive and flourishing in most Western societies. “Why not,” asks Lofland, “with Carl Jung, speak of “the achievement of death” and view dying as the final creative task of our lives?” A director of spiritual services (what used to be called a chaplain) I met recently in a hospice told me of the tremendous pressure on people to have a “good death.” This immediately evoked for me the pressure on mothers to have a “good” or “natural” birth.
Emphasising that the Happy Death Movement is still forming, Lofland identifies how the movement will make dying better. Firstly, it’s essential to talk about it. For example, the Order of the Good Death, an organisation founded by a Californian mortician, has eight tenets—and three of them concern talking about death
“2. I believe that the culture of silence around death should be broken through discussion, gatherings, art, innovation, and scholarship.
3. I believe that talking about and engaging with my inevitable death is not morbid, but displays a natural curiosity about the human condition.
7. I believe that my family and friends should know my end-of-life wishes, and that I should have the necessary paperwork to back-up those wishes.”
Secondly, death must be rearranged, moved from hospital to hospices and the home. Death in hospital is failure. Thirdly, we must legislate death with advanced decisions and assisted dying.
Lofland also identifies emerging components of the new craft of dying. Expressivity is essential, but it’s also important to not just embrace death, but to celebrate it. (I’ve done this with my talk, delivered once at the Edinburgh Festival, “Death: the upside.”) Finally—and for me surprisingly—the Happy Death Movement wants us to believe in immortality. Lofland describes how Elisabeth Kübler-Ross, who might be called the doyen of the Happy Death Movement and whose hugely influential book On Death and Dying proposed in 1969 the five stages of grief (denial, anger, bargaining, depression, and acceptance), came to believe in immortality. The pursuit of immortality, long a dream and arguably the unique selling point of Christianity, now attracts serious people and serious money.
The other two components of the emerging craft of dying are expressivity and positivity. Talk and write about your dying and coming death and celebrate your coming death and the death of those you love. New rituals will be needed, and some like “living funerals” are beginning.
Lofland is a sociologist, an academic, an observer, but you feel that she is not in fully sympathy with the Happy Death Movement. Indeed, she conjures the idea of a Dismal Death Movement to counter the Happy Death Movement: “If expressivity comes to be widely accepted as the only way to achieve a decent death, the emotionally reticent will find themselves under great pressure to ‘share.’ If the idea that death and dying provide new opportunities for self-improvement becomes common currency, the chronic under achiever will find himself facing one more opportunity for failure. Not ‘getting off’ on death may become as déclassé as sexual unresponsiveness. Then perhaps, a ‘dismal death’ movement will rise to wipe the smile from the face of death and restore the ‘Grim Reaper’ to his historic place of honor.”
There is a little about medicine and healthcare in Lofland’s book, and nor does the Order of the Good Death have much to say on the subject. But I wonder how much medicine and healthcare—gigantic, well-funded enterprises—might come to fill the need for new ways to die. Ivan Illich certainly argued that that was the case in his book Limits to Medicine, published at about the same time as Lofland’s book. Death “is now that point at which the human organism refuses any further input of treatment…Health, or the autonomous power to cope, has been expropriated down to the last breath. Technical death has won its victory over dying. Mechanical death has conquered and destroyed all other deaths.” Indeed, it is by taking on death that “health care has become a monolithic world religion.”
All those who read Lofland’s book agree that it could have been published in 2018 not 1978 and be equally relevant. The struggle to create a new craft of dying is far from over, and those of us in medicine and heath care have a particular responsibility to think and act on medicine’s role in the struggle. Almost certainly its role should be smaller.
Complete Article ↪HERE↩!
Conversations change around death, dying and funeral planning:
‘It’s not going to bring on your demise any sooner’
By Quinn Ohler
Conversations around death and dying are changing, and those in the funeral industry say it’s the baby boomer population leading the charge.
“You used to just have four funeral homes and you could choose between one or two things, [and] everybody charged basically the same thing,” says Brandy Rollins, family service manager at Trinity Funeral Homes.
Many people are looking for more options in every aspect of funeral planning from cost, to service options and final dispositions.
You are now able to personalize every aspect of your service to include what is most important to you. There’s also several options when it comes to how to dispose of your body from a traditional burial, from casket and concrete linings placed in the ground to cremation.
There’s also a movement in support of what’s called green burials, which don’t use concrete liners or embalming. Bodies are placed in a biodegradable shroud or casket.
Because there are so many options, Rollins says it is imperative that people have conversations with their loved ones about exactly what they want.
“If you don’t know what is important to the person that you are ultimately responsible for, it’s a burden to decide that,” she says.
Rollins suggests pre-planning your funeral to make it easier on your family.
“It’s a very loving act [and] it’s a very kind act,” Rollins says. “Some would argue it’s the last act of kindness you can provide.”
There’s also a push to get more people talking about their own deaths, not just for pre-planning reasons.
Death Cafes are being held around the world. The creators of the pop-up events state on their website, Death Cafes are meant to “make the most of our finite lives.”
“It’s just an aspect of life,” says Gina Vliet who has hosted Death Cafes in Edmonton.
Vliet is a member The Order of the Good Death, which encourages “staring down your death fears.” She is also an advocate for death positivity.
“Our culture is focused on living and prolonging life,” Vliet says. “I think acknowledging mortality is something people come to very organically.”
Vliet encourages people to get over the “cultural taboo” of not wanting to talk about death and dying. She is an end-of-life planning consultant who helps people plan for the final stage of life .
Vliet says that planning for your death and talking about it gives you more freedom and energy to enjoy life.
“It’s not going to bring on your demise any sooner,” Vliet says.
Both experts agree that talking about your death or the death of a loved one is a very loving act for your family, even though it can sometimes be uncomfortable.
Complete Article ↪HERE↩!