Climate change is on everyone’s mind as initiatives for renewable energy and sustainable public habits adapt to a more environmentally-friendly approach.
While numerous avenues for reducing the adverse impact of energy production and ocean contamination dominate most of the narrative around preserving the ecosystem, many more obscure and often overlooked practices lead to the accretion of environmental contaminants.
One of those areas is the traditional Western approach to burial practices and its subsequent impact on local ecosystems. Embalming fluid, typically composed of formaldehyde, ethanol, and water, is commonly used in burials throughout Western culture to preserve bodies for funeral services before being put to rest.
However, the proliferation of costly funeral services has led to increased exposure to formaldehyde, both to individuals who work with it directly and the environment. Compounding the issue is the myriad metals — such as bronze and steel — that are laid to rest during funeral services that do not readily compose in the soil. As demand for cemetery land undoubtedly grows, the adverse impact of the contaminants synonymous with funeral practices grows.
Transition Green Burials is a company focused on promoting the conversion to more eco-friendly burial practices, known as ‘green burials’ or natural burials.
Identifying Sources of Burial Pollutants
Formaldehyde produces the most concerning ecological threat with common burials practices because of its widespread use and identity as a dangerous animal carcinogen.
Highly toxic to animals, formaldehyde is implicated in cancer, nervous system disorders, and lateral sclerosis. Formaldehyde can also break down into urotropine during decomposition, an anti-bacterial chemical commonly used in antibiotics for bacterial infections, but that is harmful to the natural bacteria in the soil.
Pesticides and herbicides are often used in the internment process too, compounding the negative effects of formaldehyde on the soil surrounding burial areas. The downstream effects of the chemicals used in the internment process can eventually even lead to contamination of underground water sources.
Outside of common internment practices, cremation processes also lead to the emission of mercury and toxic plastic into the environment. Further, high carbon loads are needed for the cremation process, leading to increased carbon emissions, one of the fundamental focuses of environmental initiatives like The Paris Climate Agreement. With nearly 50 percent of Americans selecting cremation today, few realize the pollutants that are dispersed into the air from the procedure.
Many conservation groups, like the Green Burial Council, are seeking to promote more eco-friendly practices by limiting the use of embalming fluids, herbicides, and pesticides in the process. Further, some groups are promoting the use of biodegradable coffins, design to break down over time, mitigating the long-term impact of steel or brass caskets that can destroy habitats as burial grounds expand.
Transitioning to Fixed Cost Green Burials
The Green Burial Council cites the rise of certified green burial sites across the US as an indication of the legitimacy of their cause, and their emphasis on protecting worker health, reducing toxic pollutants, and promoting habitat conservation is gaining traction among various burial grounds and activists.
Similarly, Transition Green Burials is taking a hybrid approach to the issue with a focus on both the environmental impact and financial advantages of green burials through their TransitionCoin, which is designed to incentivize people to change conventional burial practices.
TransitionCoin provides a fixed cost for green burials — including all of the associated services required in the course of the burial. The targeting of a fixed price is derived from the rapidly increasing cost of funeral home services, which can reach as high as $25,000 and can lead to financial struggles among grieving families.
With a fixed cost for any green burial, people who select TransitionCoin can reduce financial costs and contribute to the growing Green Burial Movement.
The conventional burial practices among Western countries using caskets and multiple proceedings through a funeral home is also more of an isolated and recent phenomenon that began following the Civil War in the US. Several religions — including Judaism — forbid the embalming of the deceased out of religious tradition, and preserving chemicals or embalming fluid are also rarely used in Islamic burials.
Green burials grounds and services have also emerged across the US already. States like California and South Carolina have certified green burial preserves set up that are registered with the Green Burial Council. The Green Burial Council provides certified standards for funeral services, cemeteries, and burial product manufacturers. There are currently 39 states with funeral providers accredited by the Green Burial Council for eco-friendly burials.
The notion of analyzing green burial practices is one of the more obscure concepts within environmental conservation, but, nonetheless, is important to take into consideration as the widespread use of formaldehyde and pesticides continue. Transition Green Burials and the Green Burial Council are actively promoting the shift to a more eco-friendly approach, and it is beginning to gain traction among both environmental activists and funeral parlors.
Complete Article ↪HERE↩!


 In front of them stood Sally Kaplan, one of three facilitators present from the organization
In front of them stood Sally Kaplan, one of three facilitators present from the organization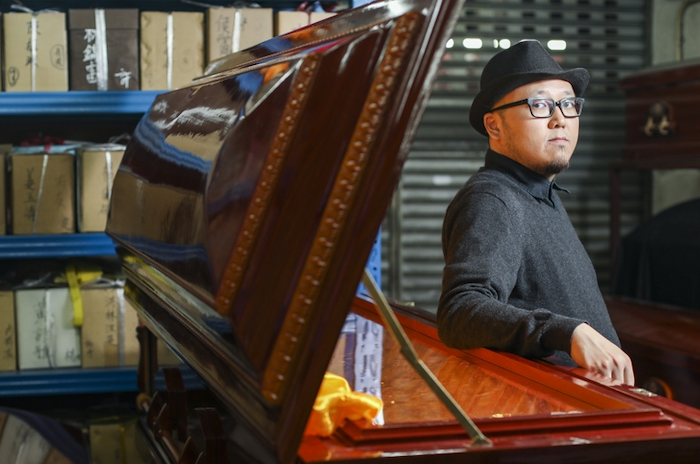 



 The object: to turn death from a feared end to something that is part of life.
The object: to turn death from a feared end to something that is part of life.
 Do: Offer the opportunity for everyone to speak but allow those who want to remain silent to do so.
Do: Offer the opportunity for everyone to speak but allow those who want to remain silent to do so.  Death doulas
Death doulas Shatzi Weisberger, an 88-year-old retired nurse from New York City is a regular, too.
Shatzi Weisberger, an 88-year-old retired nurse from New York City is a regular, too. 
